Researchers at Rutgers and Emory University are gaining insights into how schizophrenia develops by studying the strongest-known genetic risk factor.
. This dysfunction can cause energy shortfalls in the brain and result in psychiatric symptoms and disorders.
."The interplay between mitochondrial dynamics and neuronal maturation is an important area for additional detailed and rigorous study." "For genetic variants associated with schizophrenia, we want to understand the primary pathology at the," said Ryan Purcell, assistant professor of cell biology at Emory University School of Medicine and co-lead author of the study."This gives us a foothold, which may help cut through schizophrenia's polygenic complexity and better understand the neurobiology."
The finding that various schizophrenia-associated chromosomal deletions impair mitochondria runs counter to an expectation in the field that such mutations should alter proteins in the synapses that connect neurons. However, mitochondria are critical for energy-hungry synapses' function—so these models may not be in conflict.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 A study of links between fracking and health issues will be released by Pennsylvania researchersResearchers in heavily drilled Pennsylvania were preparing Tuesday to release findings from taxpayer-financed studies on possible links between the natural gas industry and pediatric cancer, asthma and poor birth outcomes.
A study of links between fracking and health issues will be released by Pennsylvania researchersResearchers in heavily drilled Pennsylvania were preparing Tuesday to release findings from taxpayer-financed studies on possible links between the natural gas industry and pediatric cancer, asthma and poor birth outcomes.
Read more »
 Kessler Foundation researchers receive $1.7 million in grants to improve lives of TBI patientsKessler Foundation scientists received four grants from the New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research, totaling nearly $1.7 million for studies based on a variety of novel approaches aimed at improving the lives of individuals with traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Kessler Foundation researchers receive $1.7 million in grants to improve lives of TBI patientsKessler Foundation scientists received four grants from the New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research, totaling nearly $1.7 million for studies based on a variety of novel approaches aimed at improving the lives of individuals with traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Read more »
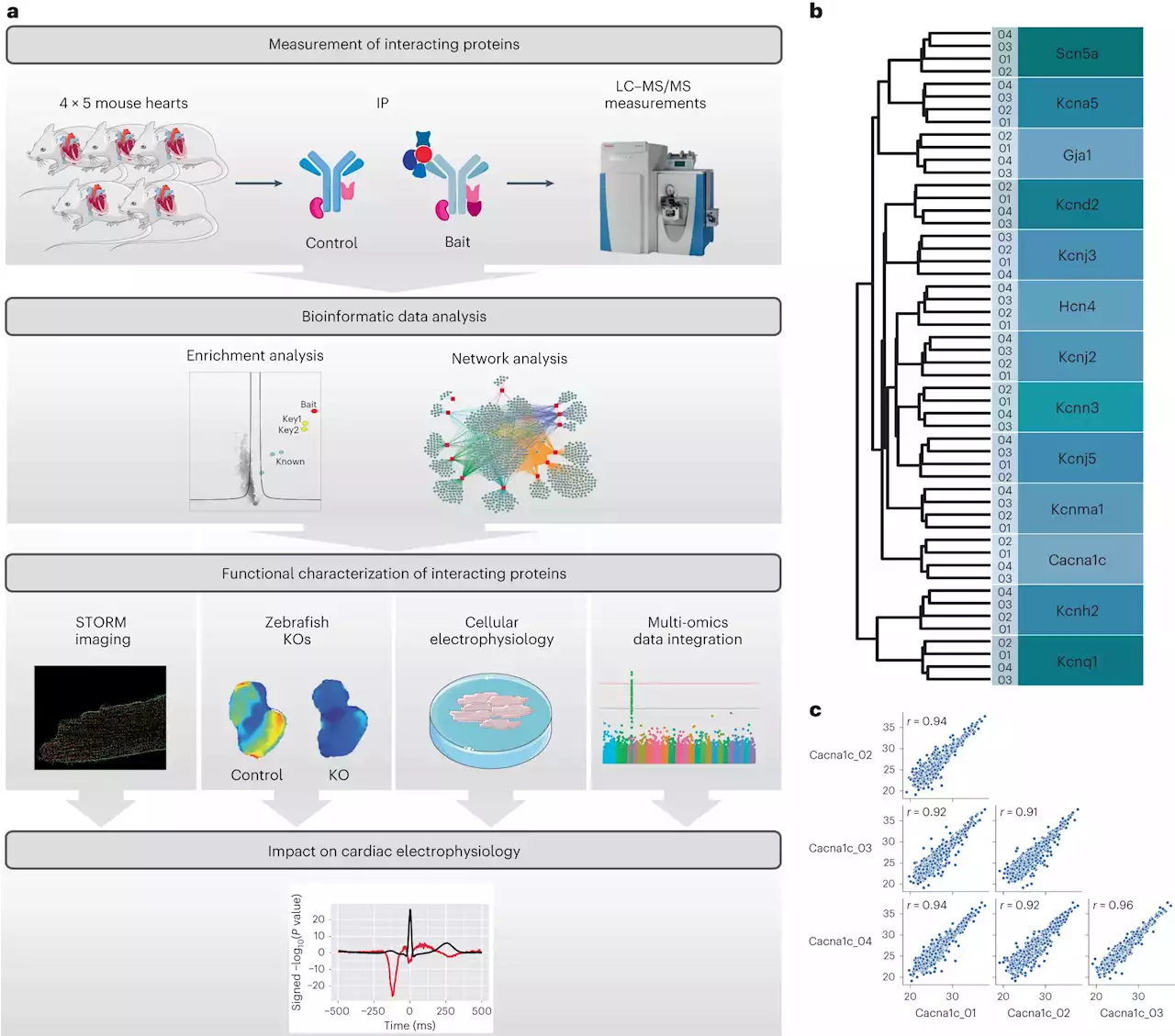 Researchers find heartbeat relies on surprisingly large network of proteinsThe first mapping of the heart's crucial ion channels reveals a surprisingly extensive network of proteins. This understanding is the first step towards more precise treatment for patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Researchers find heartbeat relies on surprisingly large network of proteinsThe first mapping of the heart's crucial ion channels reveals a surprisingly extensive network of proteins. This understanding is the first step towards more precise treatment for patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Read more »
 Researchers discover contrast dye shortage affected assessment of stroke patientsUniversity of Missouri School of Medicine neurologist Adnan Qureshi, MD recently led a study that discovered last year's iodinated media contrast dye shortage affected the assessment of stroke patients at hospitals across the country. Injecting or drinking the media contrast helps doctors see blood vessels and organs more clearly in an X-ray or a computed tomography (CT) scan.
Researchers discover contrast dye shortage affected assessment of stroke patientsUniversity of Missouri School of Medicine neurologist Adnan Qureshi, MD recently led a study that discovered last year's iodinated media contrast dye shortage affected the assessment of stroke patients at hospitals across the country. Injecting or drinking the media contrast helps doctors see blood vessels and organs more clearly in an X-ray or a computed tomography (CT) scan.
Read more »
 This simple gym exercise can help lower your blood pressure, says new studyIt requires no equipment or movement.
This simple gym exercise can help lower your blood pressure, says new studyIt requires no equipment or movement.
Read more »