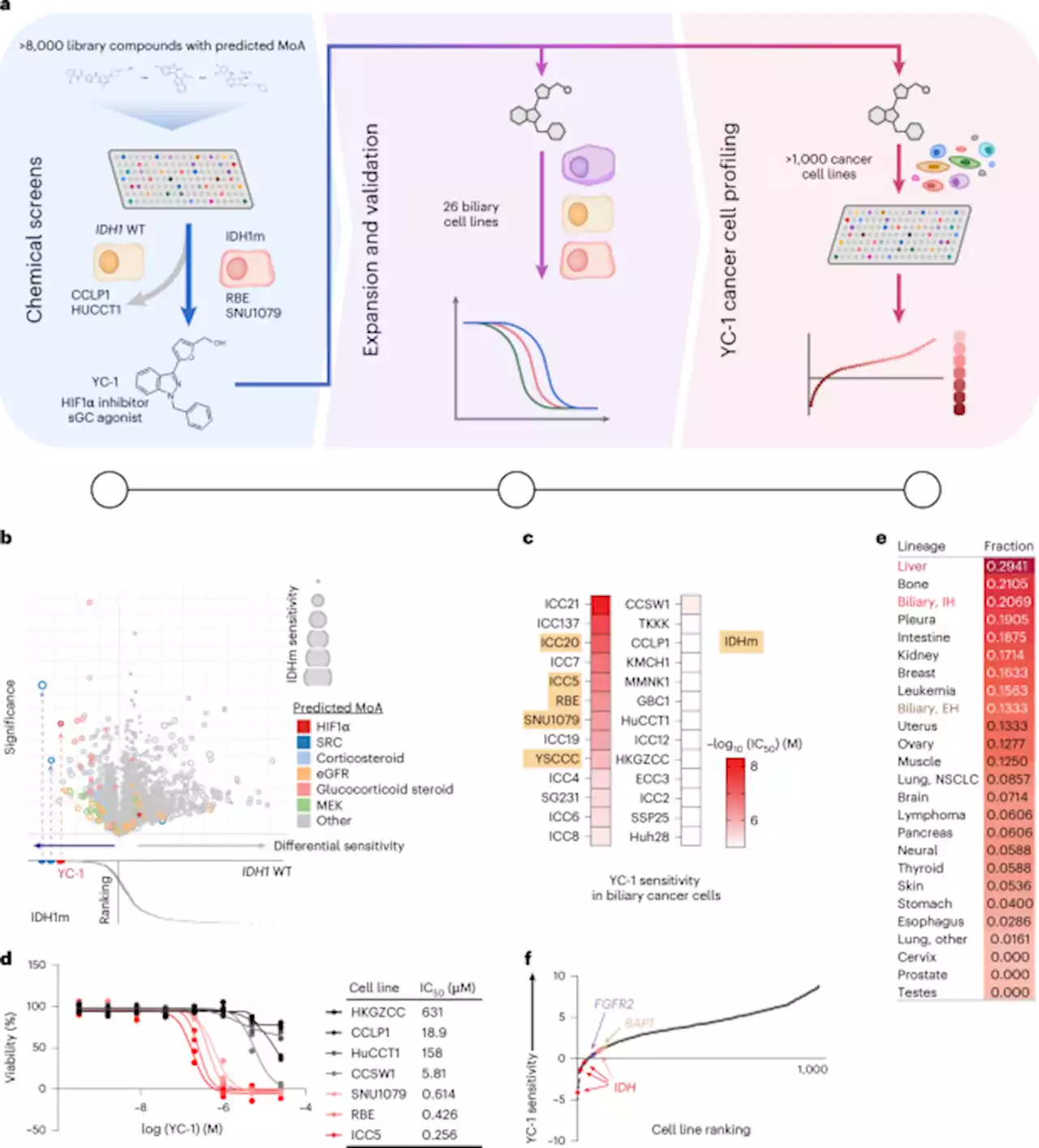
Scientists reveal a potential new approach to treating livercancer NIHforHealth naturecancer
), enriched terms from Gene Onology biological process and Gene Ontology molecular function databases were derived from EnrichR using the 500 most abundantly expressed genes based on RNA-sequencing data. The odds ratios of the enriched terms among YC-1-binding proteins were compared with the enriched terms derived using the most abundantly expressed genes. The graph in Fig.
was generated by selecting and graphing the most contrasting terms between YC-1 binders and the most abundantly expressed genes.RBE cells overexpressing SULT1A1 were treated with YC-1–biotin, YC-1–biotin + YC-1 parent competition or inactive DH-YC-1–biotin for 7–8 h. Cell lysates were prepared in nucleic acid-depleting buffer , 1 mM MgCland 1:500 benzonase from Millipore, 70746) containing protease inhibitors and phosphatase inhibitors .
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Circulating amino acid levels and colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition and UK Biobank cohorts - BMC MedicineBackground Amino acid metabolism is dysregulated in colorectal cancer patients; however, it is not clear whether pre-diagnostic levels of amino acids are associated with subsequent risk of colorectal cancer. We investigated circulating levels of amino acids in relation to colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) and UK Biobank cohorts. Methods Concentrations of 13-21 amino acids were determined in baseline fasting plasma or serum samples in 654 incident colorectal cancer cases and 654 matched controls in EPIC. Amino acids associated with colorectal cancer risk following adjustment for the false discovery rate (FDR) were then tested for associations in the UK Biobank, for which measurements of 9 amino acids were available in 111,323 participants, of which 1221 were incident colorectal cancer cases. Results Histidine levels were inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (odds ratio [OR] 0.80 per standard deviation [SD], 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.69–0.92, FDR P-value=0.03) and in UK Biobank (HR 0.93 per SD, 95% CI 0.87–0.99, P-value=0.03). Glutamine levels were borderline inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (OR 0.85 per SD, 95% CI 0.75–0.97, FDR P-value=0.08) and similarly in UK Biobank (HR 0.95, 95% CI 0.89–1.01, P=0.09) In both cohorts, associations changed only minimally when cases diagnosed within 2 or 5 years of follow-up were excluded. Conclusions Higher circulating levels of histidine were associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer in two large prospective cohorts. Further research to ascertain the role of histidine metabolism and potentially that of glutamine in colorectal cancer development is warranted.
Circulating amino acid levels and colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition and UK Biobank cohorts - BMC MedicineBackground Amino acid metabolism is dysregulated in colorectal cancer patients; however, it is not clear whether pre-diagnostic levels of amino acids are associated with subsequent risk of colorectal cancer. We investigated circulating levels of amino acids in relation to colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) and UK Biobank cohorts. Methods Concentrations of 13-21 amino acids were determined in baseline fasting plasma or serum samples in 654 incident colorectal cancer cases and 654 matched controls in EPIC. Amino acids associated with colorectal cancer risk following adjustment for the false discovery rate (FDR) were then tested for associations in the UK Biobank, for which measurements of 9 amino acids were available in 111,323 participants, of which 1221 were incident colorectal cancer cases. Results Histidine levels were inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (odds ratio [OR] 0.80 per standard deviation [SD], 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.69–0.92, FDR P-value=0.03) and in UK Biobank (HR 0.93 per SD, 95% CI 0.87–0.99, P-value=0.03). Glutamine levels were borderline inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (OR 0.85 per SD, 95% CI 0.75–0.97, FDR P-value=0.08) and similarly in UK Biobank (HR 0.95, 95% CI 0.89–1.01, P=0.09) In both cohorts, associations changed only minimally when cases diagnosed within 2 or 5 years of follow-up were excluded. Conclusions Higher circulating levels of histidine were associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer in two large prospective cohorts. Further research to ascertain the role of histidine metabolism and potentially that of glutamine in colorectal cancer development is warranted.
Read more »
 Evaluating Germline Testing Panels in Southern African Males With Advanced Prostate CancerBackground: Germline testing for prostate cancer is on the increase, with clinical implications for risk assessment, treatment, and management. Regardless of family history, NCCN recommends germline testing for patients with metastatic, regional, very-high-risk localized, and high-risk localized prostate cancer. Although African ancestry is a significant risk factor for aggressive prostate cancer, due to a lack of available data no testing criteria have been established for ethnic minorities. Patients and Methods: Through deep sequencing, we interrogated the 20 most common germline testing panel genes in 113 Black South African males presenting with largely advanced prostate cancer. Bioinformatic tools were then used to identify the pathogenicity of the variants. Results: After we identified 39 predicted deleterious variants (16 genes), further computational annotation classified 17 variants as potentially oncogenic (12 genes; 17.7% of patients). Rare pathogenic variants included CHEK2 Arg95Ter, BRCA2 Trp31Arg, ATM Arg3047Ter (2 patients), and TP53 Arg282Trp. Notable oncogenic variants of unknown pathogenicity included novel BRCA2 Leu3038Ile in a patient with early-onset disease, whereas patients with FANCA Arg504Cys and RAD51C Arg260Gln reported a family history of prostate cancer. Overall, rare pathogenic and early-onset or familial-associated oncogenic variants were identified in 6.9% (5/72) and 9.2% (8/87) of patients presenting with a Gleason score ≥8 or ≥4 + 3 prostate cancer, respectively. Conclusions: In this first-of-its-kind study of southern African males, we provide support of African inclusion for advanced, early-onset, and familial prostate cancer genetic testing, indicating clinical value for 30% of current gene panels. Recognizing current panel limitations highlights an urgent need to establish testing guidelines for men of African ancestry. We provide a rationale for considering lowering the pathologic diagnostic inclusion criteria and call for furt
Evaluating Germline Testing Panels in Southern African Males With Advanced Prostate CancerBackground: Germline testing for prostate cancer is on the increase, with clinical implications for risk assessment, treatment, and management. Regardless of family history, NCCN recommends germline testing for patients with metastatic, regional, very-high-risk localized, and high-risk localized prostate cancer. Although African ancestry is a significant risk factor for aggressive prostate cancer, due to a lack of available data no testing criteria have been established for ethnic minorities. Patients and Methods: Through deep sequencing, we interrogated the 20 most common germline testing panel genes in 113 Black South African males presenting with largely advanced prostate cancer. Bioinformatic tools were then used to identify the pathogenicity of the variants. Results: After we identified 39 predicted deleterious variants (16 genes), further computational annotation classified 17 variants as potentially oncogenic (12 genes; 17.7% of patients). Rare pathogenic variants included CHEK2 Arg95Ter, BRCA2 Trp31Arg, ATM Arg3047Ter (2 patients), and TP53 Arg282Trp. Notable oncogenic variants of unknown pathogenicity included novel BRCA2 Leu3038Ile in a patient with early-onset disease, whereas patients with FANCA Arg504Cys and RAD51C Arg260Gln reported a family history of prostate cancer. Overall, rare pathogenic and early-onset or familial-associated oncogenic variants were identified in 6.9% (5/72) and 9.2% (8/87) of patients presenting with a Gleason score ≥8 or ≥4 + 3 prostate cancer, respectively. Conclusions: In this first-of-its-kind study of southern African males, we provide support of African inclusion for advanced, early-onset, and familial prostate cancer genetic testing, indicating clinical value for 30% of current gene panels. Recognizing current panel limitations highlights an urgent need to establish testing guidelines for men of African ancestry. We provide a rationale for considering lowering the pathologic diagnostic inclusion criteria and call for furt
Read more »
 Wiltshire Great Wood to be transformed into nature reserveWiltshire Wildlife Trust purchases Great Wood, near Grittenham that covers 71 hectares.
Wiltshire Great Wood to be transformed into nature reserveWiltshire Wildlife Trust purchases Great Wood, near Grittenham that covers 71 hectares.
Read more »
 David Attenborough warns 'nature in crisis' as Scots charities bid to save itVeteran broadcaster Sir David Attenborough has warned that “nature is in crisis” as he urged people to unite behind action to save it
David Attenborough warns 'nature in crisis' as Scots charities bid to save itVeteran broadcaster Sir David Attenborough has warned that “nature is in crisis” as he urged people to unite behind action to save it
Read more »
 Britain's rivers 'emblematic' of rapidly declining nature warns head of RSPB💧 “We kind of feel a vague concern that maybe not all is well in the natural world but kind of it looks okay,” Beccy Speight told theipaper, “And actually, once you look at what’s really going on, you can see these really rapid declines”
Britain's rivers 'emblematic' of rapidly declining nature warns head of RSPB💧 “We kind of feel a vague concern that maybe not all is well in the natural world but kind of it looks okay,” Beccy Speight told theipaper, “And actually, once you look at what’s really going on, you can see these really rapid declines”
Read more »