A study published in BMCPublicHealth finds that combustible/electronic cigarette use might elevate the risk of stroke. Although preliminary, the results show concerns about the health safety of e-cigarettes and recommend further research.
Combustible or electronic cigarette use
In the questionnaire survey, the Smoking Cigarette use dataset collects recodes on cigarette use, current use, past 30-day prevalence, amount, and other related smoking details. Participants were asked whether they had smoked at least 100 cigarettes in their entire life and their current smoking habits . Participants were asked whether they used e-cigarettes even once .
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Nurses strikes underway as health bosses ask public to 'use services wisely'Health bosses have asked people to 'use services wisely' as the latest round of nurses strikes in the county get underway.
Nurses strikes underway as health bosses ask public to 'use services wisely'Health bosses have asked people to 'use services wisely' as the latest round of nurses strikes in the county get underway.
Read more »
 BMC Roadmachine TWOReview: BMC Roadmachine TWO - Really fun, if quite stiff for an endurance bike. cycling Ride_BMC
BMC Roadmachine TWOReview: BMC Roadmachine TWO - Really fun, if quite stiff for an endurance bike. cycling Ride_BMC
Read more »
 Altered expression of anti-apoptotic protein Api5 affects breast tumorigenesis - BMC CancerBackground Apoptosis or programmed cell death plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis and, therefore, is a tightly regulated process. Deregulation of apoptosis signalling can favour carcinogenesis. Apoptosis inhibitor 5 (Api5), an inhibitor of apoptosis, is upregulated in cancers. Interestingly, Api5 is shown to regulate both apoptosis and cell proliferation. To address the precise functional significance of Api5 in carcinogenesis here we investigate the role of Api5 in breast carcinogenesis. Methods Initially, we carried out in silico analyses using TCGA and GENT2 datasets to understand expression pattern of API5 in breast cancer patients followed by investigating the protein expression in Indian breast cancer patient samples. To investigate the functional importance of Api5 in breast carcinogenesis, we utilised MCF10A 3D breast acinar cultures and spheroid cultures of malignant breast cells with altered Api5 expression. Various phenotypic and molecular changes induced by altered Api5 expression were studied using these 3D culture models. Furthermore, in vivo tumorigenicity studies were used to confirm the importance of Api5 in breast carcinogenesis. Results In-silico analysis revealed elevated levels of Api5 transcript in breast cancer patients which correlated with poor prognosis. Overexpression of Api5 in non-tumorigenic breast acinar cultures resulted in increased proliferation and cells exhibited a partial EMT-like phenotype with higher migratory potential and disruption in cell polarity. Furthermore, during acini development, the influence of Api5 is mediated via the combined action of FGF2 activated PDK1-Akt/cMYC signalling and Ras-ERK pathways. Conversely, Api5 knock-down downregulated FGF2 signalling leading to reduced proliferation and diminished in vivo tumorigenic potential of the breast cancer cells. Conclusion Taken together, our study identifies Api5 as a central player involved in regulating multiple events during breast carcinogenesis includi
Altered expression of anti-apoptotic protein Api5 affects breast tumorigenesis - BMC CancerBackground Apoptosis or programmed cell death plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis and, therefore, is a tightly regulated process. Deregulation of apoptosis signalling can favour carcinogenesis. Apoptosis inhibitor 5 (Api5), an inhibitor of apoptosis, is upregulated in cancers. Interestingly, Api5 is shown to regulate both apoptosis and cell proliferation. To address the precise functional significance of Api5 in carcinogenesis here we investigate the role of Api5 in breast carcinogenesis. Methods Initially, we carried out in silico analyses using TCGA and GENT2 datasets to understand expression pattern of API5 in breast cancer patients followed by investigating the protein expression in Indian breast cancer patient samples. To investigate the functional importance of Api5 in breast carcinogenesis, we utilised MCF10A 3D breast acinar cultures and spheroid cultures of malignant breast cells with altered Api5 expression. Various phenotypic and molecular changes induced by altered Api5 expression were studied using these 3D culture models. Furthermore, in vivo tumorigenicity studies were used to confirm the importance of Api5 in breast carcinogenesis. Results In-silico analysis revealed elevated levels of Api5 transcript in breast cancer patients which correlated with poor prognosis. Overexpression of Api5 in non-tumorigenic breast acinar cultures resulted in increased proliferation and cells exhibited a partial EMT-like phenotype with higher migratory potential and disruption in cell polarity. Furthermore, during acini development, the influence of Api5 is mediated via the combined action of FGF2 activated PDK1-Akt/cMYC signalling and Ras-ERK pathways. Conversely, Api5 knock-down downregulated FGF2 signalling leading to reduced proliferation and diminished in vivo tumorigenic potential of the breast cancer cells. Conclusion Taken together, our study identifies Api5 as a central player involved in regulating multiple events during breast carcinogenesis includi
Read more »
 The association of maternal anaemia with adverse maternal and foetal outcomes in Somali women: a prospective study - BMC Women's HealthBackground Anaemia in pregnant women is one of the most common public health problems, especially in low- and middle-income countries, such as Somalia. This study aimed to examine the association between the severity of anaemia during pregnancy and the risk of adverse maternal and foetal outcomes in Somali women. Methods We prospectively enrolled pregnant women who had deliveries from May 1 to December 1, 2022, at Mogadishu Somali Turkey Recep Tayyip Erdoğan Training and Research Hospital. Blood haemoglobin levels were measured for each participant at admission for delivery. Anaemia was defined as a haemoglobin level of less than 11 g/dL, with mild (10 to 10.9 g/dL), moderate (7 to 9.9 g/dL), and severe (| 7 g/dL) forms. The associations between maternal anaemia and maternal-foetal outcomes were investigated. Results The study included 1186 consecutive pregnant women (mean age 26.9 years, range 16–47). The incidence of maternal anaemia at delivery was 64.8%, with 33.8%, 59.8%, and 6.4% of women having mild, moderate and severe forms, respectively. Anaemia at delivery was associated with increased oxytocin administration to prompt labour (OR, 2.25, 95% CI, 1.34–3.78). Both moderate and severe anaemia were associated with increased risks for postpartum haemorrhage (moderate, OR, 4.93; severe, OR, 41.30) and the need for maternal blood transfusions (moderate, OR, 9.66; severe, OR, 301.50). In addition, severe anaemia was associated with increased risks for preterm delivery (OR, 2.50, 95% CI, 1.35–4.63), low birth weight (OR, 3.45, 95% CI, 1.87–6.35), stillbirths (OR, 4.02, 95% CI, 1.79–8.98), placental abruption (OR, 58.04,95% CI, 6.83–493.27) and maternal ICU admission (OR, 8.33, 95% CI, 3.53–19.63). Conclusion Our findings suggest that anaemia in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal and foetal outcomes, with moderate or severe anaemia leading to increased risks for peri-, intra- and postpartum complications and that treatment of severe anaemia in pregnant wo
The association of maternal anaemia with adverse maternal and foetal outcomes in Somali women: a prospective study - BMC Women's HealthBackground Anaemia in pregnant women is one of the most common public health problems, especially in low- and middle-income countries, such as Somalia. This study aimed to examine the association between the severity of anaemia during pregnancy and the risk of adverse maternal and foetal outcomes in Somali women. Methods We prospectively enrolled pregnant women who had deliveries from May 1 to December 1, 2022, at Mogadishu Somali Turkey Recep Tayyip Erdoğan Training and Research Hospital. Blood haemoglobin levels were measured for each participant at admission for delivery. Anaemia was defined as a haemoglobin level of less than 11 g/dL, with mild (10 to 10.9 g/dL), moderate (7 to 9.9 g/dL), and severe (| 7 g/dL) forms. The associations between maternal anaemia and maternal-foetal outcomes were investigated. Results The study included 1186 consecutive pregnant women (mean age 26.9 years, range 16–47). The incidence of maternal anaemia at delivery was 64.8%, with 33.8%, 59.8%, and 6.4% of women having mild, moderate and severe forms, respectively. Anaemia at delivery was associated with increased oxytocin administration to prompt labour (OR, 2.25, 95% CI, 1.34–3.78). Both moderate and severe anaemia were associated with increased risks for postpartum haemorrhage (moderate, OR, 4.93; severe, OR, 41.30) and the need for maternal blood transfusions (moderate, OR, 9.66; severe, OR, 301.50). In addition, severe anaemia was associated with increased risks for preterm delivery (OR, 2.50, 95% CI, 1.35–4.63), low birth weight (OR, 3.45, 95% CI, 1.87–6.35), stillbirths (OR, 4.02, 95% CI, 1.79–8.98), placental abruption (OR, 58.04,95% CI, 6.83–493.27) and maternal ICU admission (OR, 8.33, 95% CI, 3.53–19.63). Conclusion Our findings suggest that anaemia in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal and foetal outcomes, with moderate or severe anaemia leading to increased risks for peri-, intra- and postpartum complications and that treatment of severe anaemia in pregnant wo
Read more »
 The Effects of Forgiveness on Our Mental HealthTyler Vanderweele of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health joins Current to discuss the results of his new study showing the positive impact forgiveness has on your mental health.
The Effects of Forgiveness on Our Mental HealthTyler Vanderweele of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health joins Current to discuss the results of his new study showing the positive impact forgiveness has on your mental health.
Read more »
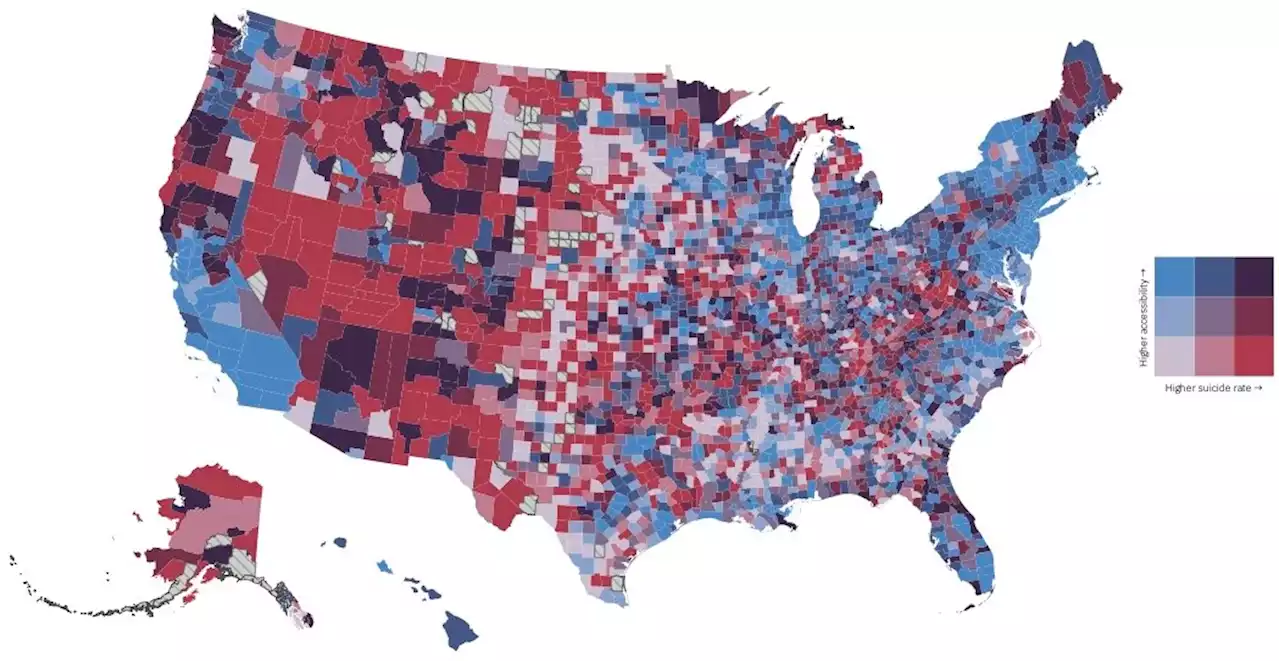 Study finds that improved access to mental health care is associated with reductions in suicide riskAmid historically high suicide rates and mental health care provider shortages, new research from Incite at Columbia University suggests that interventions to alleviate mental health care access disparities can prevent unnecessary death and suffering. In an article pending publication in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences next week, 'Differential Spatial-Social Accessiblity to Mental Health Care and Suicide,' Daniel Tadmon and Peter S. Bearman find that in the United States improved access to mental health care is associated with reductions in suicide risk.
Study finds that improved access to mental health care is associated with reductions in suicide riskAmid historically high suicide rates and mental health care provider shortages, new research from Incite at Columbia University suggests that interventions to alleviate mental health care access disparities can prevent unnecessary death and suffering. In an article pending publication in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences next week, 'Differential Spatial-Social Accessiblity to Mental Health Care and Suicide,' Daniel Tadmon and Peter S. Bearman find that in the United States improved access to mental health care is associated with reductions in suicide risk.
Read more »
