Researchers conducted a systematic review of the literature investigating the associations between lifestyle, health behaviors, and health outcomes.
By Hugo Francisco de SouzaAug 23 2023Reviewed by Sophia Coveney In a recent study published in the journal BMC Public Health, researchers conducted a systematic review of the literature investigating the associations between lifestyle, health behaviors, and health outcomes.
Additionally, evidence suggests that health behaviors have synergistic effects more significant than the sum of each behavior in isolation, especially in depression and anxiety risk, psychological distress, and weight changes. Reviewers employed this search strategy on three online databases, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, from databased initiation until July 2022. Inclusion criteria were age , study methodology , and publication language .
Bias assessment was conducted using recommendations from the Cochrane Handbook for observational studies. Every included study was assessed for bias risk in the following domains:“ selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, selective reporting bias, and other factors that may increase the risk of bias.”
“Risk of bias was conducted for all included studies. For both study types, between 5 and 30% had a high-risk judgment across all domains, while low-risk judgment varied between ~50–90%. Some of the domains had an unclear judgment due to lack of information ”
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 NUS researchers harness nature's design to develop novel pressure sensorResearchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have developed a novel aero-elastic pressure sensor, called 'eAir'.
NUS researchers harness nature's design to develop novel pressure sensorResearchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have developed a novel aero-elastic pressure sensor, called 'eAir'.
Read more »
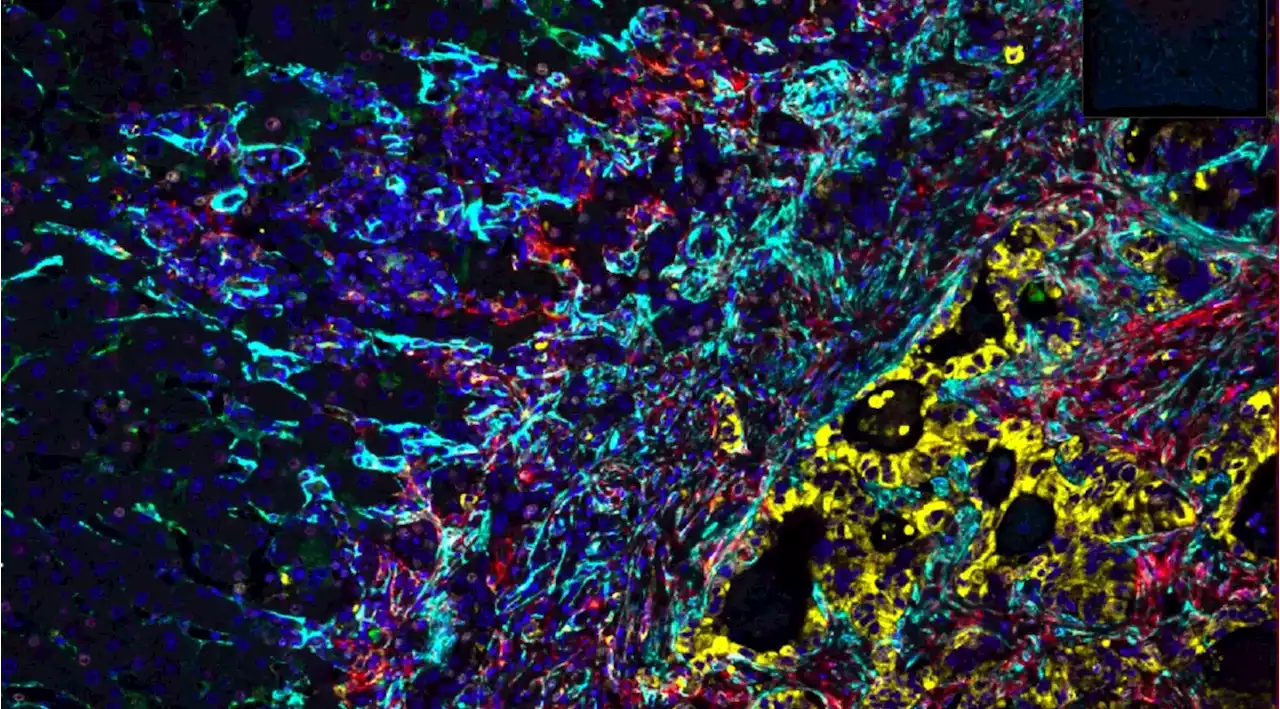 Researchers find capsules surrounding liver metastases of colorectal cancer are a healing response by the liverA study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and physicians from Karolinska Hospital shows that a capsule of connective tissue around liver metastases from colorectal cancer improves patient survival and represents a healing response by the liver, not a phenomenon caused by the tumor itself.
Researchers find capsules surrounding liver metastases of colorectal cancer are a healing response by the liverA study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and physicians from Karolinska Hospital shows that a capsule of connective tissue around liver metastases from colorectal cancer improves patient survival and represents a healing response by the liver, not a phenomenon caused by the tumor itself.
Read more »
 Researchers discover potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr virusScientists at The Wistar Institute have discovered a potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr Virus, and their study results are published in the journal mBio.
Researchers discover potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr virusScientists at The Wistar Institute have discovered a potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr Virus, and their study results are published in the journal mBio.
Read more »
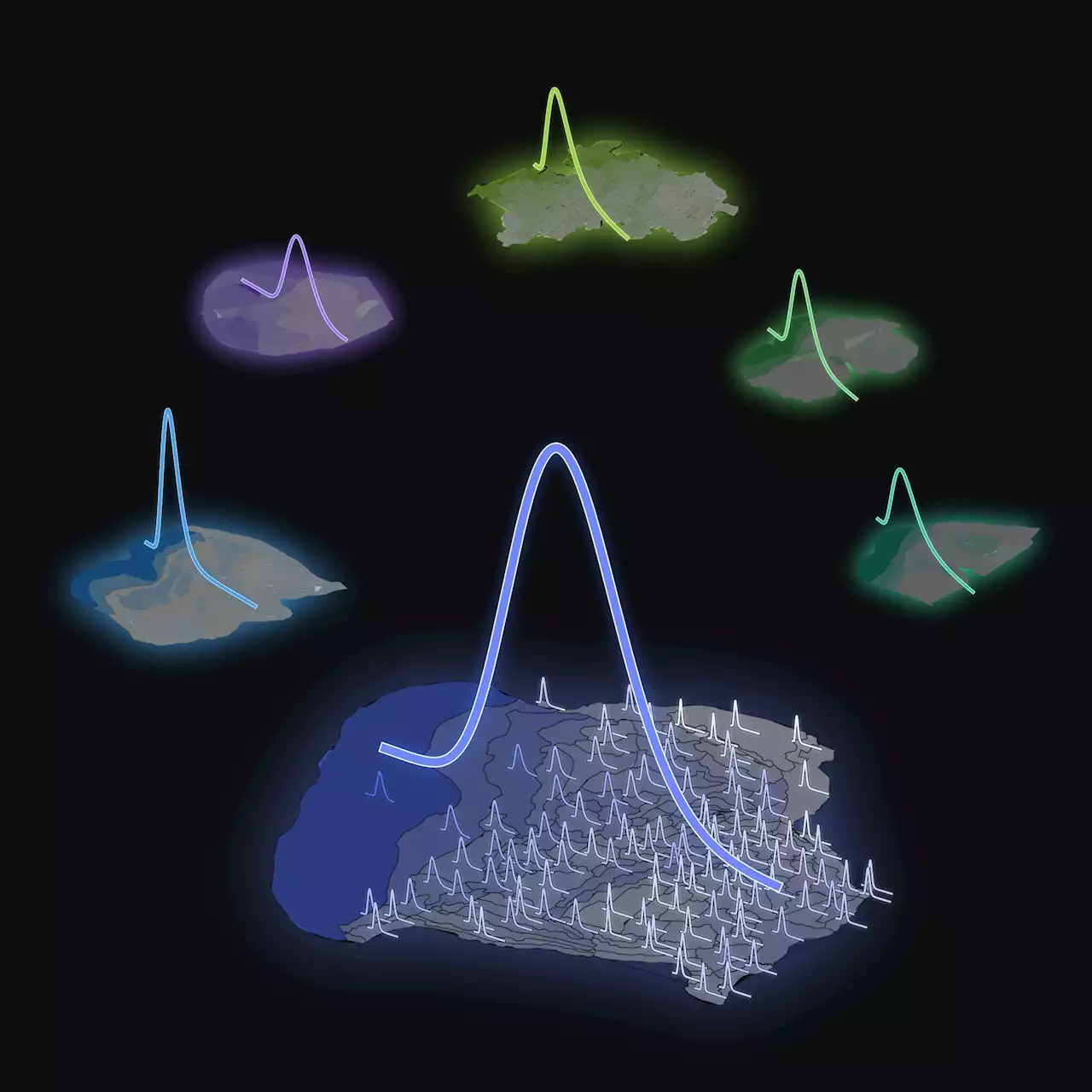 Researchers identify mathematical rule behind the distribution of neurons in our brainsHuman Brain Project (HBP) researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich and the University of Cologne (Germany) have uncovered how neuron densities are distributed across and within cortical areas in the mammalian brain. They have unveiled a fundamental organizational principle of cortical cytoarchitecture: the ubiquitous lognormal distribution of neuron densities.
Researchers identify mathematical rule behind the distribution of neurons in our brainsHuman Brain Project (HBP) researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich and the University of Cologne (Germany) have uncovered how neuron densities are distributed across and within cortical areas in the mammalian brain. They have unveiled a fundamental organizational principle of cortical cytoarchitecture: the ubiquitous lognormal distribution of neuron densities.
Read more »
 UAB researchers secure PCORI funding to compare two pathways of post-fracture patient careIn osteoporosis, bones become brittle and fragile, putting them at high risk of fractures or breaks. These 'fragility fractures' can cause pain, suffering, disability and even death, and patients have increased risks of repeat fractures.
UAB researchers secure PCORI funding to compare two pathways of post-fracture patient careIn osteoporosis, bones become brittle and fragile, putting them at high risk of fractures or breaks. These 'fragility fractures' can cause pain, suffering, disability and even death, and patients have increased risks of repeat fractures.
Read more »
 Researchers detect heart damage in kids gaming for too longAcademics said the impact of sitting for periods of six hours could be setting the stage for heart attacks and strokes
Researchers detect heart damage in kids gaming for too longAcademics said the impact of sitting for periods of six hours could be setting the stage for heart attacks and strokes
Read more »
