Weill Cornell Medicine has received a five-year, $12.4 million grant from the National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, for an extensive program of basic and translational research on the biology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common form of lymphoma.
Weill Cornell Medicine Aug 15 2024 Weill Cornell Medicine has received a five-year, $12.4 million grant from the National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, for an extensive program of basic and translational research on the biology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma , the most common form of lymphoma.
DLBCL represents a significant challenge for cancer biologists because about 40% of patients either don't respond well to initial chemotherapy or end up relapsing. Response rates also can vary dramatically among different DLBCL subtypes. Researchers expect that the development of significantly better treatments will require a more comprehensive understanding of the complex processes that trigger and sustain the disease.
As part of the newly funded research program, the researchers intend to reveal this lymphomagenesis process in unprecedented detail, showing how different combinations of gene mutations and interactions with partner immune cells can combine to turn germinal center B cells into different DLBCL subtypes.
Related StoriesThe researchers expect their progress in understanding DLBCL origins to illuminate vulnerabilities in these cancers that can be exploited with new and precise treatments—with emphasis on milder, non-chemotherapy treatments that will be more tolerable, especially for older patients. For example, Dr. Cerchietti and colleagues aim to develop methods for reprogramming lymph node-resident T cells so that they attack DLBCL cells.
Medicine Research Antibody Cancer Cell Chemotherapy Gene Hematology Lymph Node Myeloma Oncology Preclinical
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
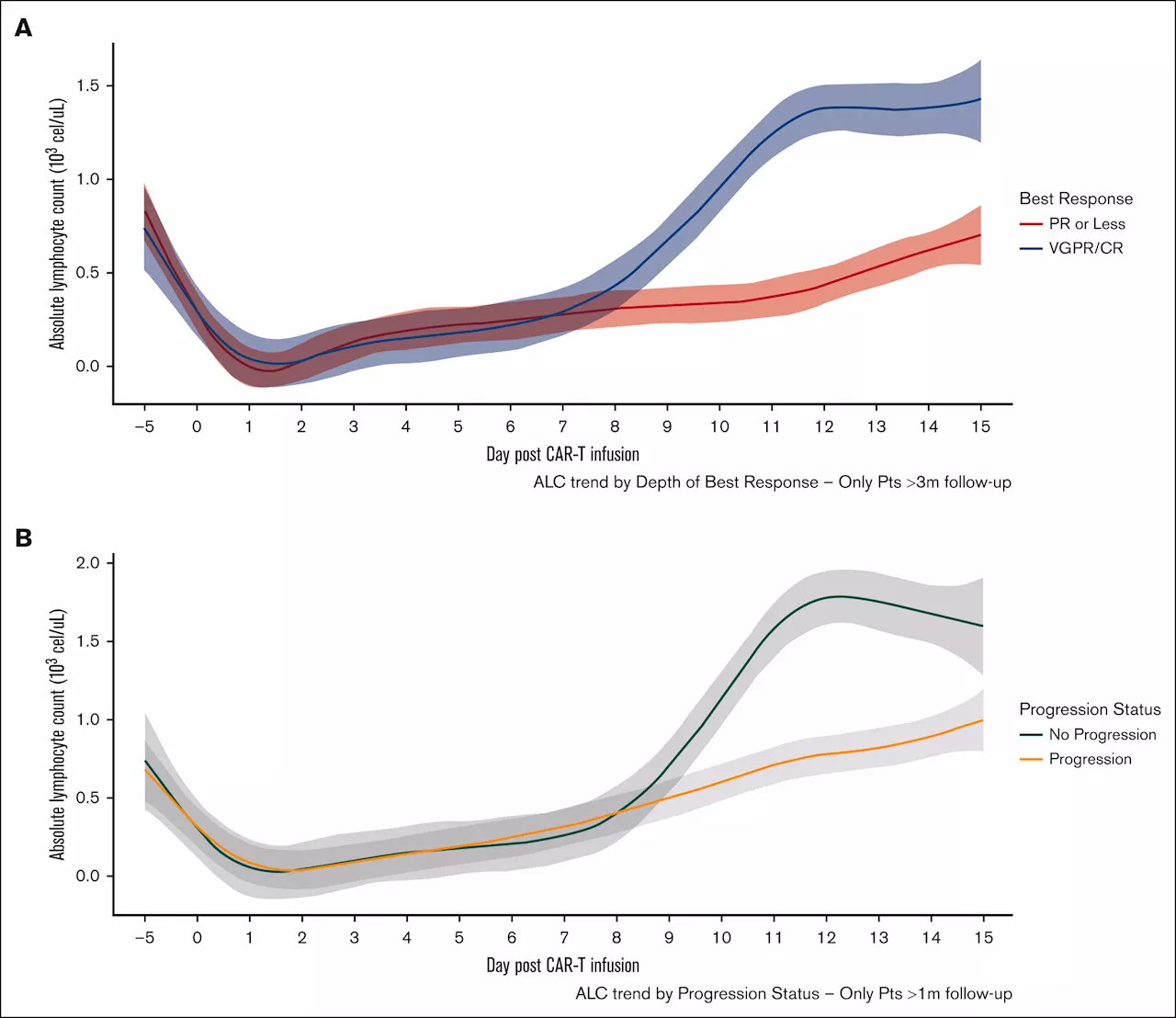 Blood test may guide use of multiple myeloma immunotherapyA simple blood test that measures the number of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell in the body, may predict whether people who have relapsed multiple myeloma are going to respond well to CAR-T immunotherapy, according to new research from Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian, Columbia University and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount...
Blood test may guide use of multiple myeloma immunotherapyA simple blood test that measures the number of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell in the body, may predict whether people who have relapsed multiple myeloma are going to respond well to CAR-T immunotherapy, according to new research from Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian, Columbia University and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount...
Read more »
 Simple blood test may predict CAR-T therapy success in multiple myelomaA simple blood test that measures the number of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell in the body, may predict whether people who have relapsed multiple myeloma are going to respond well to CAR-T immunotherapy, according to new research from Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian, Columbia University and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount...
Simple blood test may predict CAR-T therapy success in multiple myelomaA simple blood test that measures the number of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell in the body, may predict whether people who have relapsed multiple myeloma are going to respond well to CAR-T immunotherapy, according to new research from Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian, Columbia University and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount...
Read more »
 ‘Kamala Harris is the embodiment of the Obama coalition’ says political strategistWe speak to pollster and political strategist Cornell Belcher.
‘Kamala Harris is the embodiment of the Obama coalition’ says political strategistWe speak to pollster and political strategist Cornell Belcher.
Read more »
 New preclinical model offers a unique platform for studying Parkinson's disease processA new preclinical model offers a unique platform for studying the Parkinson's disease process and suggests a relatively easy method for detecting the disease in people, according to a new study led by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers.
New preclinical model offers a unique platform for studying Parkinson's disease processA new preclinical model offers a unique platform for studying the Parkinson's disease process and suggests a relatively easy method for detecting the disease in people, according to a new study led by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers.
Read more »
 Preclinical model offers new insights into Parkinson's disease processA new preclinical model offers a unique platform for studying the Parkinson's disease process and suggests a relatively easy method for detecting the disease in people, according to a new study led by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers.
Preclinical model offers new insights into Parkinson's disease processA new preclinical model offers a unique platform for studying the Parkinson's disease process and suggests a relatively easy method for detecting the disease in people, according to a new study led by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers.
Read more »
 New dual-chamber wireless pacemaker shows reliable performance in clinical trialA dual-chamber wireless pacemaker provides reliable performance over three months, bolstering evidence for this new pacemaker option, according to results from a multi-center, international clinical trial co-led by a Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigator.
New dual-chamber wireless pacemaker shows reliable performance in clinical trialA dual-chamber wireless pacemaker provides reliable performance over three months, bolstering evidence for this new pacemaker option, according to results from a multi-center, international clinical trial co-led by a Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigator.
Read more »
