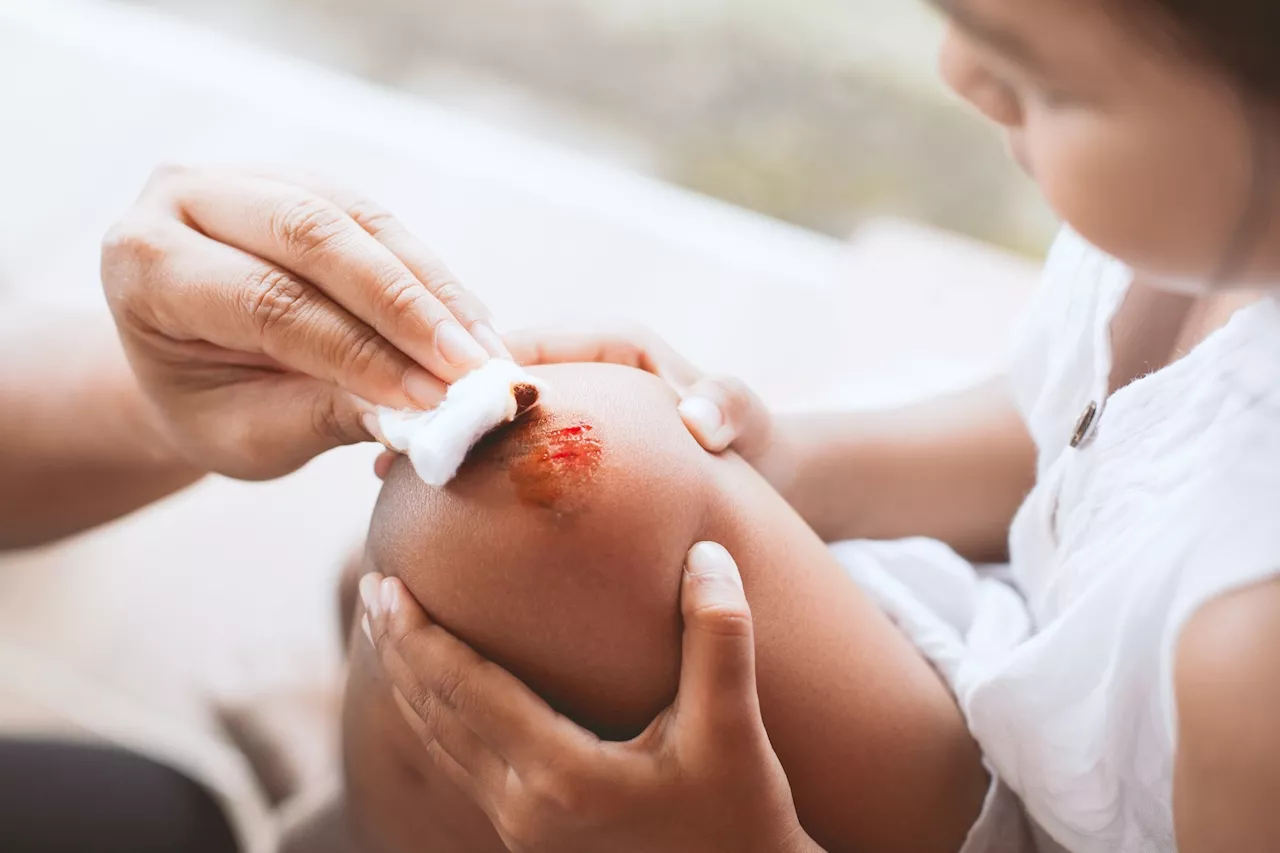
Study explores how wound microbiota affect skin repair and infection risk by altering host immune responses, underscoring the complexity of microbial interactions in wound healing.
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D.Apr 7 2024Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. In a recent Nature Reviews Microbiology study, researchers review how the wound microbiota interferes with skin repair processes and facilitates infection onset by modulating host immune responses.
The wound-healing process involves coagulation, hemostasis, inflammation, cell proliferation and migration, and tissue remodeling. Any alteration to these processes can lead to delayed wound healing and the development of a chronic wound. Both exogenous and endogenous microorganisms can contaminate an open wound. The wound can facilitate microbial growth by exposing subcutaneous tissues and nutrients, which can subsequently lead to the colonization of microorganisms in the wound. This type of colonization can cause local infection and biofilm formation, which has the potential to spread to other tissues and organs.
Staphylococcus aureus also produces pore-forming toxins that disrupt the host cell membrane to prevent immune clearance. Furthermore, serine proteases produced by this bacterium act as enterotoxins that induce chronic inflammation and create severe, non-healing diabetic wounds. Streptococcus Streptococcus spp., including β-Hemolytic group A streptococci , group B streptococci , and group C streptococci, can be found in invasive and non-invasive wounds.
Fungi Candida albicans is a fungal species most commonly found in chronic, surgical, and burn wounds. These fungi can enter host cells by binding to E-cadherin and triggering endocytosis. The pathogenicity of C. albicans is dependent on its ability to switch between yeast and a highly invasive hyphal phenotype.
Antibiotic Antibiotic Resistance Bacteria Burn Cell Cell Proliferation Chemicals Chronic Diabetes Fungi Hemostasis Infection Control Inflammation Microbiology Obesity Proliferation Skin Staphylococcus Aureus Toxins Wound Care Wound Healing
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
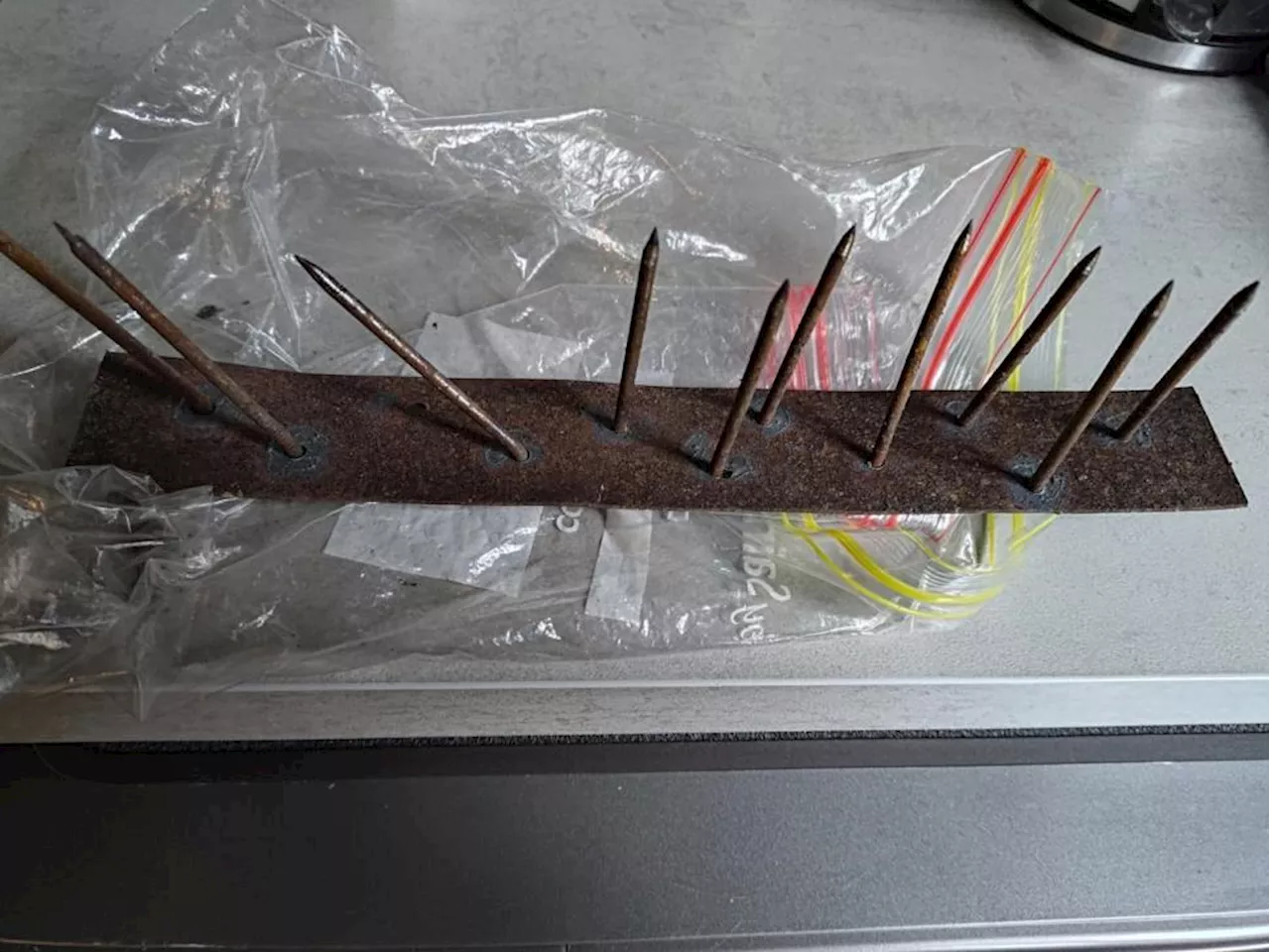 Cyclist suffers puncture wound after riding over homemade nail trap hidden on popular trailCyclist suffers puncture wound from homemade nail trap
Cyclist suffers puncture wound after riding over homemade nail trap hidden on popular trailCyclist suffers puncture wound from homemade nail trap
Read more »
 Innovative plasma-activated hydrogel dressings revolutionize chronic wound careAn effective treatment for chronic wounds that does not involve antibiotics, but an ionized gas to activate a wound dressing, has been developed by a team of international scientists.
Innovative plasma-activated hydrogel dressings revolutionize chronic wound careAn effective treatment for chronic wounds that does not involve antibiotics, but an ionized gas to activate a wound dressing, has been developed by a team of international scientists.
Read more »
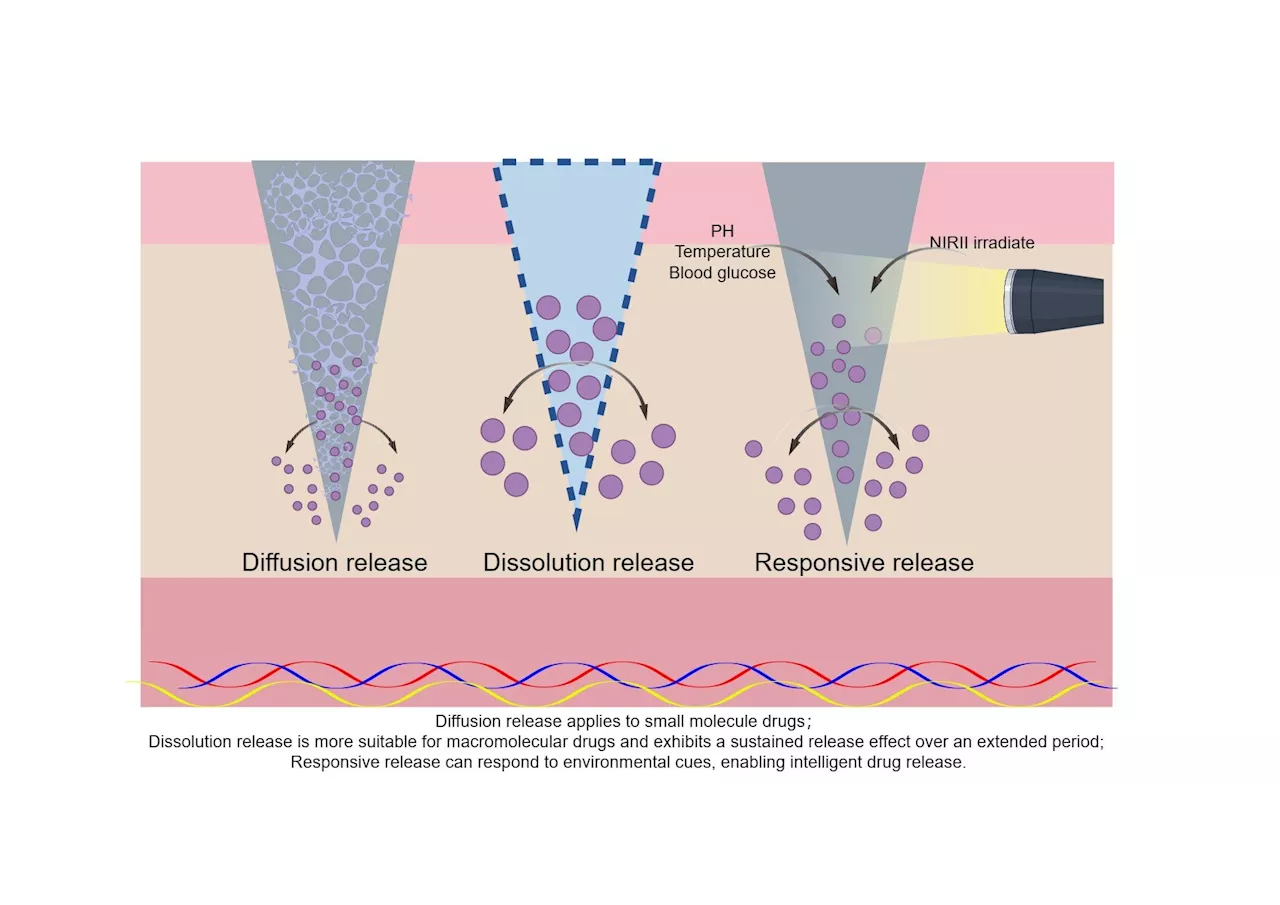 Promoting diabetic wound healing using microneedlesThe global population of patients with diabetic wounds is expected to rise to between 9.1 million and 26.1 million by 2030. Diabetic wounds severely impact patients' quality of life, both physically and mentally, while also imposing a substantial economic burden on health care systems.
Promoting diabetic wound healing using microneedlesThe global population of patients with diabetic wounds is expected to rise to between 9.1 million and 26.1 million by 2030. Diabetic wounds severely impact patients' quality of life, both physically and mentally, while also imposing a substantial economic burden on health care systems.
Read more »
 Harnessing biomaterial-based FTY720 immunotherapy to accelerate oral wound healingA study aiming to deliver Fingolimod (FTY720) loaded polymer scaffolds to enhance oral wound healing by modulating pro-regenerative immune cell migration associated with improved vascularization and tissue remodeling was presented at the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American...
Harnessing biomaterial-based FTY720 immunotherapy to accelerate oral wound healingA study aiming to deliver Fingolimod (FTY720) loaded polymer scaffolds to enhance oral wound healing by modulating pro-regenerative immune cell migration associated with improved vascularization and tissue remodeling was presented at the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American...
Read more »
 Advanced hydrogel promotes GI wound healingGastrointestinal (GI) surgery, interventional screening procedures such as colonoscopies, and naturally occurring complications such as ulcers, can lead to adverse events, including internal bleeding, intestinal wall perforation, and leakage.
Advanced hydrogel promotes GI wound healingGastrointestinal (GI) surgery, interventional screening procedures such as colonoscopies, and naturally occurring complications such as ulcers, can lead to adverse events, including internal bleeding, intestinal wall perforation, and leakage.
Read more »
 SolasCure Awarded £405K Innovate UK Biomedical Catalyst Grant to Advance Chronic Wound CareSOLASCURE Ltd (SolasCure), a biotechnology company developing a novel treatment to transform chronic wound care, today announced it has been awarded a highly competitive Biomedical Catalyst grant for...
SolasCure Awarded £405K Innovate UK Biomedical Catalyst Grant to Advance Chronic Wound CareSOLASCURE Ltd (SolasCure), a biotechnology company developing a novel treatment to transform chronic wound care, today announced it has been awarded a highly competitive Biomedical Catalyst grant for...
Read more »