A study published in BMCOralHealth finds that periodontal status and oral hygiene deteriorates in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes patients. A multidisciplinary approach is needed to maintain periodontal health in such patients.
Thornton-Evans G, Eke P, Wei L, Palmer A, Moeti R, Hutchins S, et al. Periodontitis among adults aged ≥ 30 years - United States, 2009–2010. MMWR Suppl. 2013;22:129–35.
Ronnie Levine, Catherine Stillman-Lowe. The scientific basis of oral Health Education . 8th ed. Springer; 2018. Pattayil S, Vadakkekuttical RJ, Radhakrishnan C, Kanakkath H, Hrishi TS. Proportional relationship between periodontal inflamed surface area, clinical attachment loss, and glycated hemoglobin level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on insulin therapy and on oral antidiabetic therapy. J Periodontol. 2023;3:31–40.
SingleCare Team. The 411 on A1C: Normal A1C levels and 15 ways to lower high A1C [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 Apr 16]. Available from:Reddy CVK, Maurya M. A comparative study to assess the oral health status and treatment needs of diabetics and non-diabetic population attending some of the hospitals in Mysore City. Journal of Indian Association of Public Health Dentistry [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Apr 14];6:1–14.
Chee B, Park B, Bartold MP. Periodontitis and type II diabetes: a two-way relationship. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2013;11:317–29. Preshaw PM, Alba AL, Herrera D, Jepsen S, Konstantinidis A, Makrilakis K et al. Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship. Diabetologia 2012;55:21–31.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Combined oral antibiotics and intrauterine perfusion can improve in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer pregnancy outcomes in patients with chronic endometritis and repeated embryo implantation failure - BMC Women's HealthBackground The aim of this retrospective study was to investigate whether oral antibiotics (doxycycline and metronidazole) combined with intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin and dexamethasone) are beneficial for patients with repeated implantation failure (RIF) and chronic endometritis (CE) to improve clinical pregnancy outcomes. Methods Patients with RIF and CE were diagnosed using hysteroscopy and histology together. A total of 42 patients were enrolled in the study. All patients received oral antibiotics (doxycycline combined with metronidazole) and 22 patients underwent intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin combined with dexamethasone) immediately after the end of oral antibiotic therapy. Pregnancy outcomes were evaluated during the first in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer (ET) cycle. Results For the first D3 ET after treatment with oral antibiotics (doxycycline and metronidazole) combined with intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin and dexamethasone), higher embryo implantation rate (30.95% vs. 26.67%, P = 0.0308), clinical pregnancy rate (30% vs. 50%, P | 0.001), live birth rate (33.33% vs. 45.45%, P | 0.0001). No fetal malformations or ectopic pregnancies were observed. Conclusion We report oral antibiotics (doxycycline and metronidazole) combined with intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin and dexamethasone) as a novel treatment for CE to improve the outcomes of successful pregnancy compared with those of oral antibiotics alone.
Combined oral antibiotics and intrauterine perfusion can improve in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer pregnancy outcomes in patients with chronic endometritis and repeated embryo implantation failure - BMC Women's HealthBackground The aim of this retrospective study was to investigate whether oral antibiotics (doxycycline and metronidazole) combined with intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin and dexamethasone) are beneficial for patients with repeated implantation failure (RIF) and chronic endometritis (CE) to improve clinical pregnancy outcomes. Methods Patients with RIF and CE were diagnosed using hysteroscopy and histology together. A total of 42 patients were enrolled in the study. All patients received oral antibiotics (doxycycline combined with metronidazole) and 22 patients underwent intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin combined with dexamethasone) immediately after the end of oral antibiotic therapy. Pregnancy outcomes were evaluated during the first in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer (ET) cycle. Results For the first D3 ET after treatment with oral antibiotics (doxycycline and metronidazole) combined with intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin and dexamethasone), higher embryo implantation rate (30.95% vs. 26.67%, P = 0.0308), clinical pregnancy rate (30% vs. 50%, P | 0.001), live birth rate (33.33% vs. 45.45%, P | 0.0001). No fetal malformations or ectopic pregnancies were observed. Conclusion We report oral antibiotics (doxycycline and metronidazole) combined with intrauterine perfusion (gentamicin and dexamethasone) as a novel treatment for CE to improve the outcomes of successful pregnancy compared with those of oral antibiotics alone.
Read more »
 Comparison of fasting and random lipid profiles among subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an outpatient-based cross-sectional study in Bangladesh - Diabetology & Metabolic SyndromeBackground Despite the wide acceptability of fasting lipid profiles in practice, emerging evidence suggests that random lipid profiles might be a convenient alternative for lipid measurement. The objective of the present study was to compare the fasting and random lipid profile among subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Methods The present cross-sectional study included 1543 subjects with T2DM visiting several endocrinology outpatient clinics throughout Bangladesh from January to December 2021. The fasting lipid profile was measured in the morning following 8–10 h of overnight fasting, and the random lipid profile was measured at any time of the day, irrespective of the last meal. The values of fasting and random lipids were compared using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Spearman rank correlation coefficients. Results In this study, a good level of correlation was observed between fasting and random lipid levels [r = 0.793, p | 0.001 for triglyceride (TG); r = 0.873, p | 0.001 for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C); r = 0.609, p | 0.001 for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C); and r = 0.780, p | 0.001 for total cholesterol (TC)]. In addition, TG and TC levels increased by 14% and 0.51%, respectively, in the random state compared to the fasting state (p- |0.05), while LDL-C levels decreased by 0.71% (p-value 0.42). No change was noticed in the HDL-C level. The difference between fasting and random lipid profiles was similar irrespective of patients’ age, sex, BMI, glucose-lowering drug(s), and lipid-lowering therapy. Conclusions Random lipid profile correlates significantly with fasting lipid profile with little difference. Hence, it might be a reliable alternative for fasting lipid profile in patients with T2DM.
Comparison of fasting and random lipid profiles among subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an outpatient-based cross-sectional study in Bangladesh - Diabetology & Metabolic SyndromeBackground Despite the wide acceptability of fasting lipid profiles in practice, emerging evidence suggests that random lipid profiles might be a convenient alternative for lipid measurement. The objective of the present study was to compare the fasting and random lipid profile among subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Methods The present cross-sectional study included 1543 subjects with T2DM visiting several endocrinology outpatient clinics throughout Bangladesh from January to December 2021. The fasting lipid profile was measured in the morning following 8–10 h of overnight fasting, and the random lipid profile was measured at any time of the day, irrespective of the last meal. The values of fasting and random lipids were compared using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Spearman rank correlation coefficients. Results In this study, a good level of correlation was observed between fasting and random lipid levels [r = 0.793, p | 0.001 for triglyceride (TG); r = 0.873, p | 0.001 for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C); r = 0.609, p | 0.001 for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C); and r = 0.780, p | 0.001 for total cholesterol (TC)]. In addition, TG and TC levels increased by 14% and 0.51%, respectively, in the random state compared to the fasting state (p- |0.05), while LDL-C levels decreased by 0.71% (p-value 0.42). No change was noticed in the HDL-C level. The difference between fasting and random lipid profiles was similar irrespective of patients’ age, sex, BMI, glucose-lowering drug(s), and lipid-lowering therapy. Conclusions Random lipid profile correlates significantly with fasting lipid profile with little difference. Hence, it might be a reliable alternative for fasting lipid profile in patients with T2DM.
Read more »
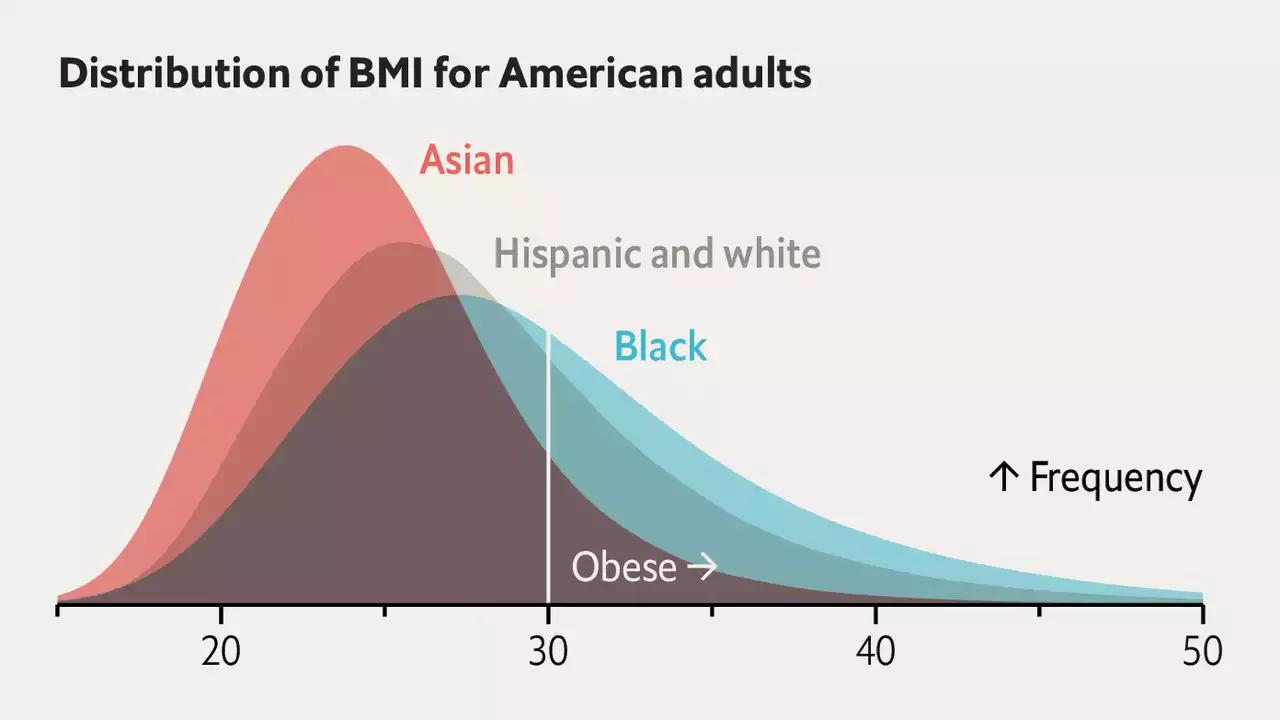 Prescription rules for obesity drugs may unfairly exclude non-whitesPotent new anti-obesity drugs can reduce body weight by 15-20%. However, regulation and costs limit who can take them
Prescription rules for obesity drugs may unfairly exclude non-whitesPotent new anti-obesity drugs can reduce body weight by 15-20%. However, regulation and costs limit who can take them
Read more »
