Austocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest.
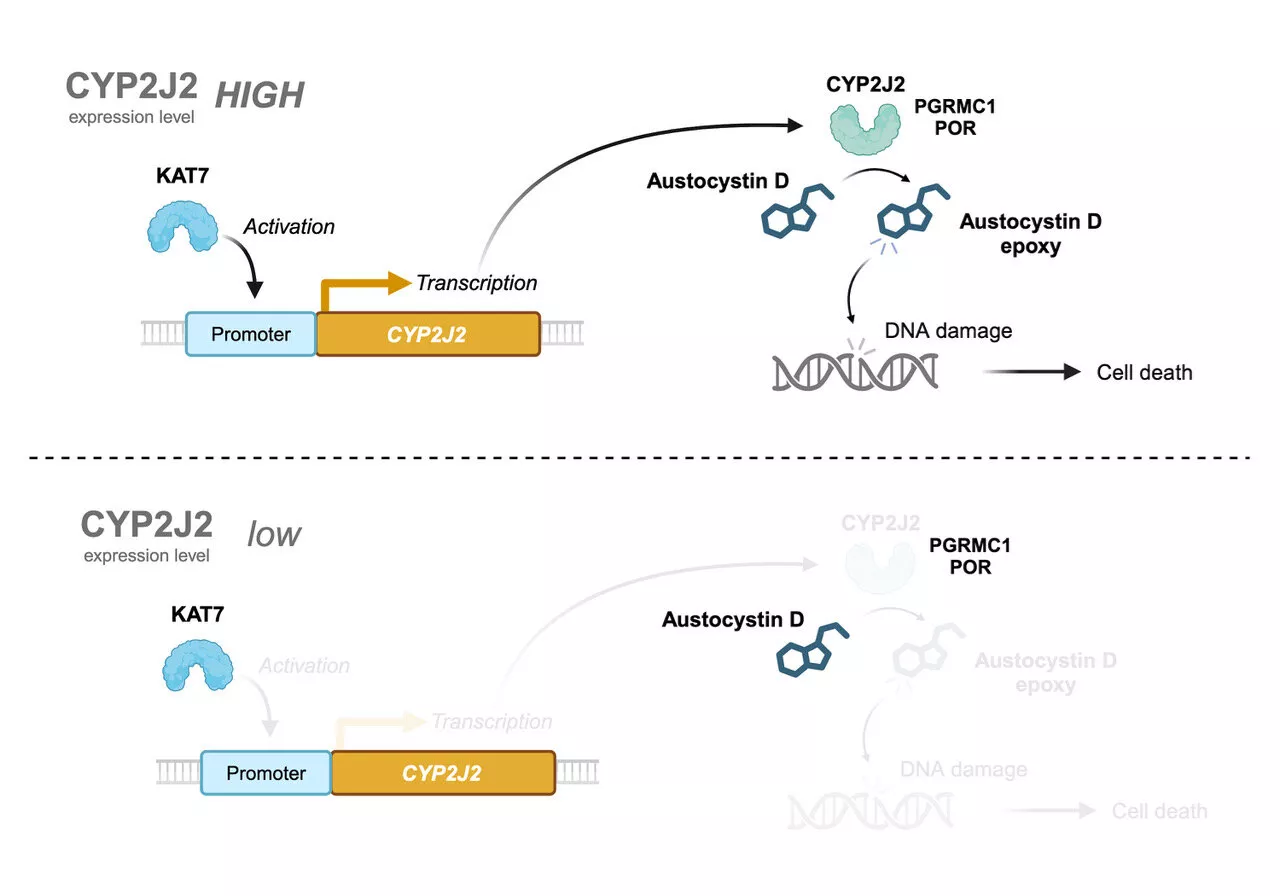
Tokyo University of ScienceAug 27 2024 Austocystin D promotes cell death by damaging their DNA , a process which might be dependent on cytochrome P450 oxygenase enzymes. Notably, austocystin D has shown significant activity against cancer cells with increased CYP expression. However, the specific role and function of the CYP2J2 enzyme in the cytotoxicity of austocystin D remain to be determined.
Initially, the researchers utilized data from the Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research 39 to analyze the correlation between austocystin D sensitivity and CYP expression in cancer cells. By analyzing gene markers in these cells, they found that the expression of one particular CYP gene, namely CYP2J2, positively correlated with sensitivity to austocystin D.
Furthermore, the researchers conducted a series of experiments to analyze the effects of overexpression and depletion of CYP2J2 on austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicity. Their results confirmed that overexpression of CYP2J2 enhanced the cytotoxic effects of austocystin D, while its depletion resulted in reduced sensitivity to austocystin D and significantly less cytotoxicity in cancer cells.
We are hopeful that our novel findings on austocystin D and its association with CYP2J2 can lead to the development of safe and effective therapeutic agents for patients with cancer, especially those with high CYP2J2 expression levels."
Bone Bone Cancer Cancer Cell Cell Death Cell Proliferation Compound Cytochrome P450 DNA DNA Damage Enzyme Fungi Gene Lysine Proliferation Research Technology Transcription
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Cancer research explores role of cytochrome oxygenases in augmenting austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicityAustocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest.
Cancer research explores role of cytochrome oxygenases in augmenting austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicityAustocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest.
Read more »
 Cancer research explores role of cytochrome oxygenases in augmenting austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicityAustocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest.
Cancer research explores role of cytochrome oxygenases in augmenting austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicityAustocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest.
Read more »
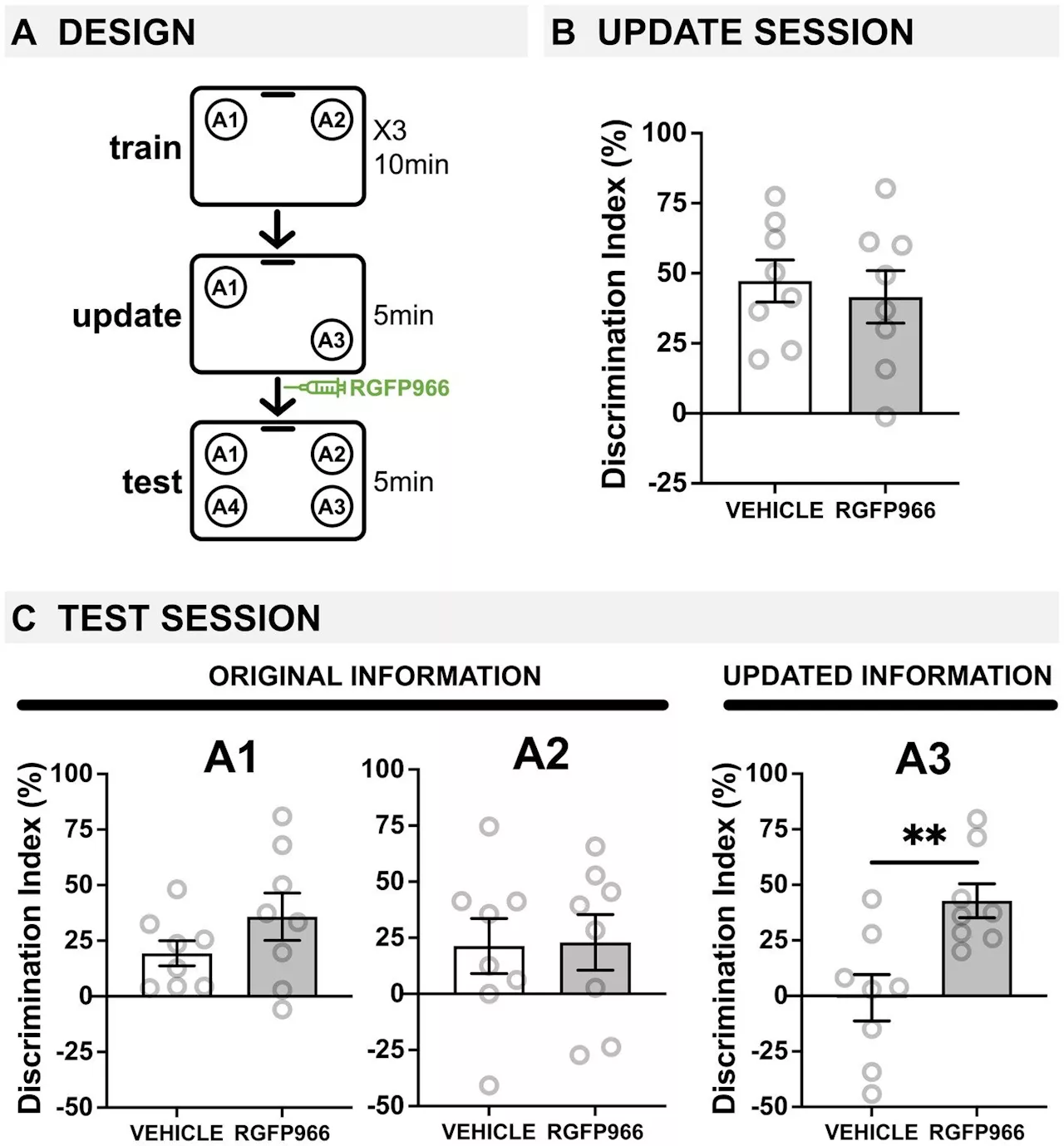 Memory problems in old age linked to a key enzyme, study in mice findsEveryone has moments of forgetfulness from time to time, especially as we get older. But older adults don't just have difficulty remembering new information. They also have a harder time modifying those memories when new details emerge. Yet, little is known about the mechanisms behind memory updating and how those mechanisms go awry with age.
Memory problems in old age linked to a key enzyme, study in mice findsEveryone has moments of forgetfulness from time to time, especially as we get older. But older adults don't just have difficulty remembering new information. They also have a harder time modifying those memories when new details emerge. Yet, little is known about the mechanisms behind memory updating and how those mechanisms go awry with age.
Read more »
 Inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis impacts cognitive functionThe inflammatory activity in the body caused by rheumatoid arthritis is linked to specific cognitive impairments, finds a small comparative study, published in the open access journal RMD Open.
Inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis impacts cognitive functionThe inflammatory activity in the body caused by rheumatoid arthritis is linked to specific cognitive impairments, finds a small comparative study, published in the open access journal RMD Open.
Read more »
 Inflammatory activity of rheumatoid arthritis linked to specific cognitive impairmentsThe inflammatory activity in the body caused by rheumatoid arthritis is linked to specific cognitive impairments, finds a small comparative study, published in the open access journal RMD Open.
Inflammatory activity of rheumatoid arthritis linked to specific cognitive impairmentsThe inflammatory activity in the body caused by rheumatoid arthritis is linked to specific cognitive impairments, finds a small comparative study, published in the open access journal RMD Open.
Read more »
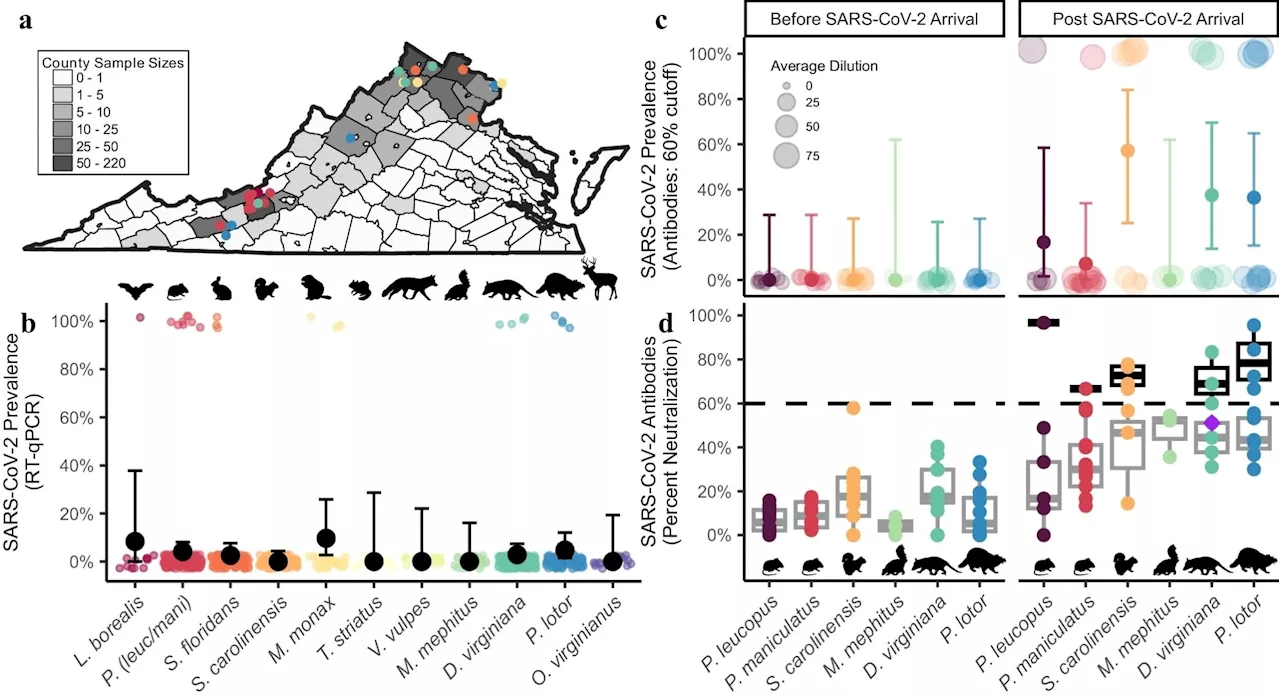 Wildlife species show high SARS-CoV-2 exposure linked to human activityResearchers found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in six wildlife species and higher seroprevalence in high human activity areas. Seven new human-to-animal transmission events of the Omicron variant were identified.
Wildlife species show high SARS-CoV-2 exposure linked to human activityResearchers found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in six wildlife species and higher seroprevalence in high human activity areas. Seven new human-to-animal transmission events of the Omicron variant were identified.
Read more »