A genetic connection between cardiovascular disease and psoriasis highlights shared inflammatory pathways, emphasizing the need for cardiovascular monitoring.
By Pooja Toshniwal PahariaReviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.Sep 19 2024 New research reveals a genetic connection between cardiovascular disease and psoriasis, suggesting shared inflammatory mechanisms. The findings may guide future treatments for both conditions and underscore the importance of monitoring cardiovascular health in psoriasis patients.
Psoriasis is an excellent model for investigating this interaction since severe psoriasis is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease development. Cardiovascular risk factors, obesity, and dyslipidemia are common in the psoriasis community, particularly in those with severe cases. About the study In the present genetic association study, researchers examined the bidirectional links between genetic estimators of cardiovascular illness and IMIDs like psoriasis.
The primary study outcomes included the associations between genetic estimators of coronary artery disease and stroke and risks of psoriatic disease and nine other IMIDs. Mendelian randomizations with inverse variance weighting determined the associations. The data analysis period went from January 2023 until May 2024.
Results The analysis comprised 181,249 patients with CAD and 1,165,690 control individuals, 110,182 patients of stroke and 1,503,898 control individuals, and 36,466 patients of psoriasis and 458,078 control individuals among nearly 3,400,000 people. Contrasting prior assumptions, genetic estimators of psoriasis showed no relationship with stroke or CAD. Reverse association analyses showed that genetic estimators of stroke and CAD showed risk-enhancing relationships with psoriasis.
Sensitivity analyses and confounding adjustments produced similar findings. There were no differences in stroke or CAD Mendelian randomization effects on psoriasis between subgroups based on gender or HLA-C*06:02 status. Individuals on angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, β-blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers , aspirin, or statins did not have increased effects on psoriasis from cardiovascular MR.
Psoriasis Angiotensin Arthritis Blood Cardiology Chronic Coronary Artery Disease Dyslipidemia Genetic Inflammation Inflammatory Bowel Disease Obesity Research Rheumatoid Arthritis Skin Skin Cells Stroke
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 The role of the Mediterranean diet in cardiovascular disease preventionResearchers perform an updated review of recent studies to evaluate the effectiveness of the Mediterranean Diet in preventing cardiovascular disease.
The role of the Mediterranean diet in cardiovascular disease preventionResearchers perform an updated review of recent studies to evaluate the effectiveness of the Mediterranean Diet in preventing cardiovascular disease.
Read more »
 New tool could revolutionize cardiovascular risk management: PRESS score validatedThe association between platelet hyperreactivity and the risk of cardiovascular events.
New tool could revolutionize cardiovascular risk management: PRESS score validatedThe association between platelet hyperreactivity and the risk of cardiovascular events.
Read more »
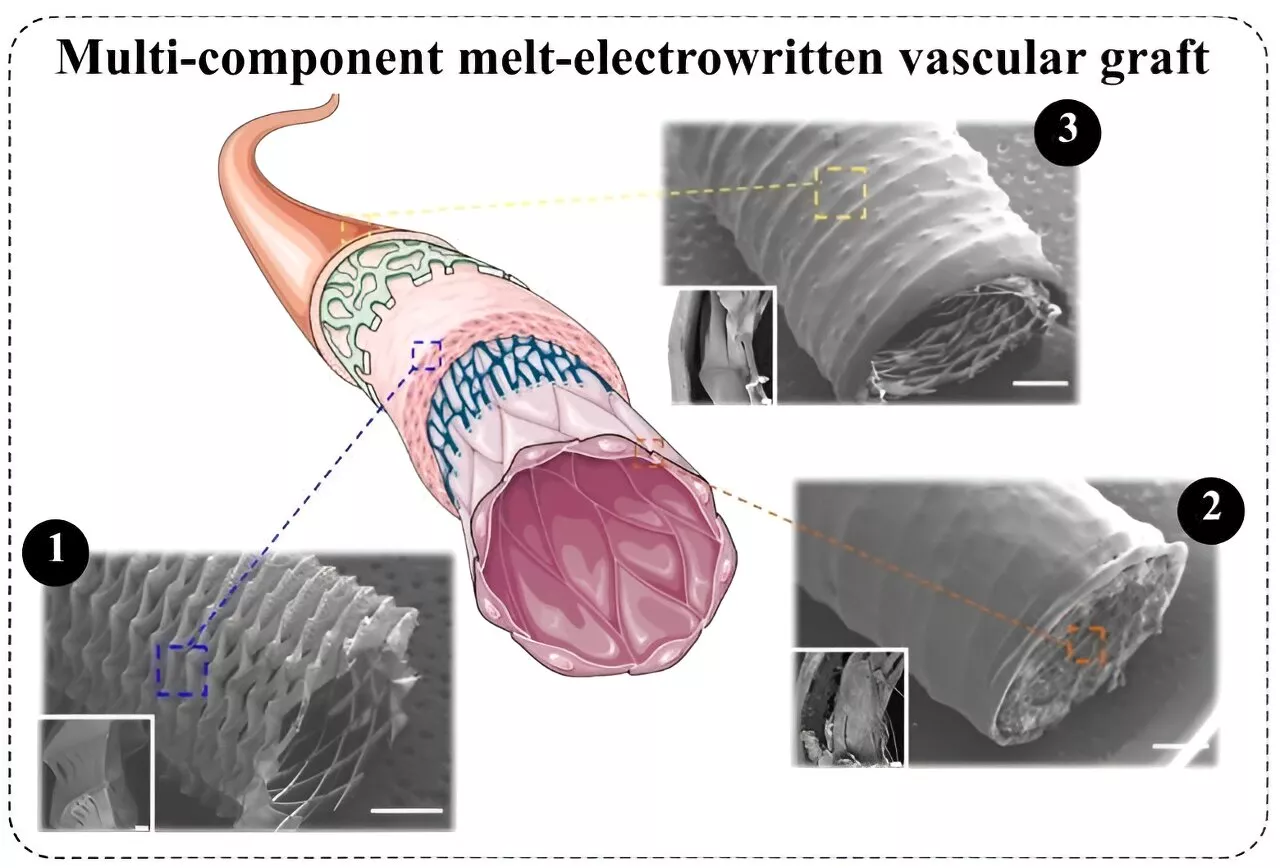 Bioengineers develop hybrid grafts to combat cardiovascular diseaseResearchers from AMBER and Trinity, led by Dr. David Hoey, have successfully replicated the behavior of a blood vessel and its guiding structure to regenerate damaged tissue.
Bioengineers develop hybrid grafts to combat cardiovascular diseaseResearchers from AMBER and Trinity, led by Dr. David Hoey, have successfully replicated the behavior of a blood vessel and its guiding structure to regenerate damaged tissue.
Read more »
 New insights into blood flow fluctuations offer hope in fight against cardiovascular diseaseResearchers have uncovered how fluctuations in blood flow that occur when there is a narrowing in the arteries contribute to harmful inflammation and blood clot formation, revealing the critical role that blood flow–driven forces play in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases.
New insights into blood flow fluctuations offer hope in fight against cardiovascular diseaseResearchers have uncovered how fluctuations in blood flow that occur when there is a narrowing in the arteries contribute to harmful inflammation and blood clot formation, revealing the critical role that blood flow–driven forces play in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases.
Read more »
 Semaglutide shown to cut major adverse cardiovascular events in heart failure patientsSemaglutide shows promise in reducing cardiovascular risks in obese patients with heart failure, improving outcomes in a recent large-scale clinical trial.
Semaglutide shown to cut major adverse cardiovascular events in heart failure patientsSemaglutide shows promise in reducing cardiovascular risks in obese patients with heart failure, improving outcomes in a recent large-scale clinical trial.
Read more »
 Menopause potentially linked to adverse cardiovascular health through blood fat profile changesNew research presented at the ESC Congress 2024 in London, UK (30 August—2 September) shows that women in the menopause transition period show changes in their blood cholesterol profiles which could have an adverse impact on their cardiovascular health.
Menopause potentially linked to adverse cardiovascular health through blood fat profile changesNew research presented at the ESC Congress 2024 in London, UK (30 August—2 September) shows that women in the menopause transition period show changes in their blood cholesterol profiles which could have an adverse impact on their cardiovascular health.
Read more »
