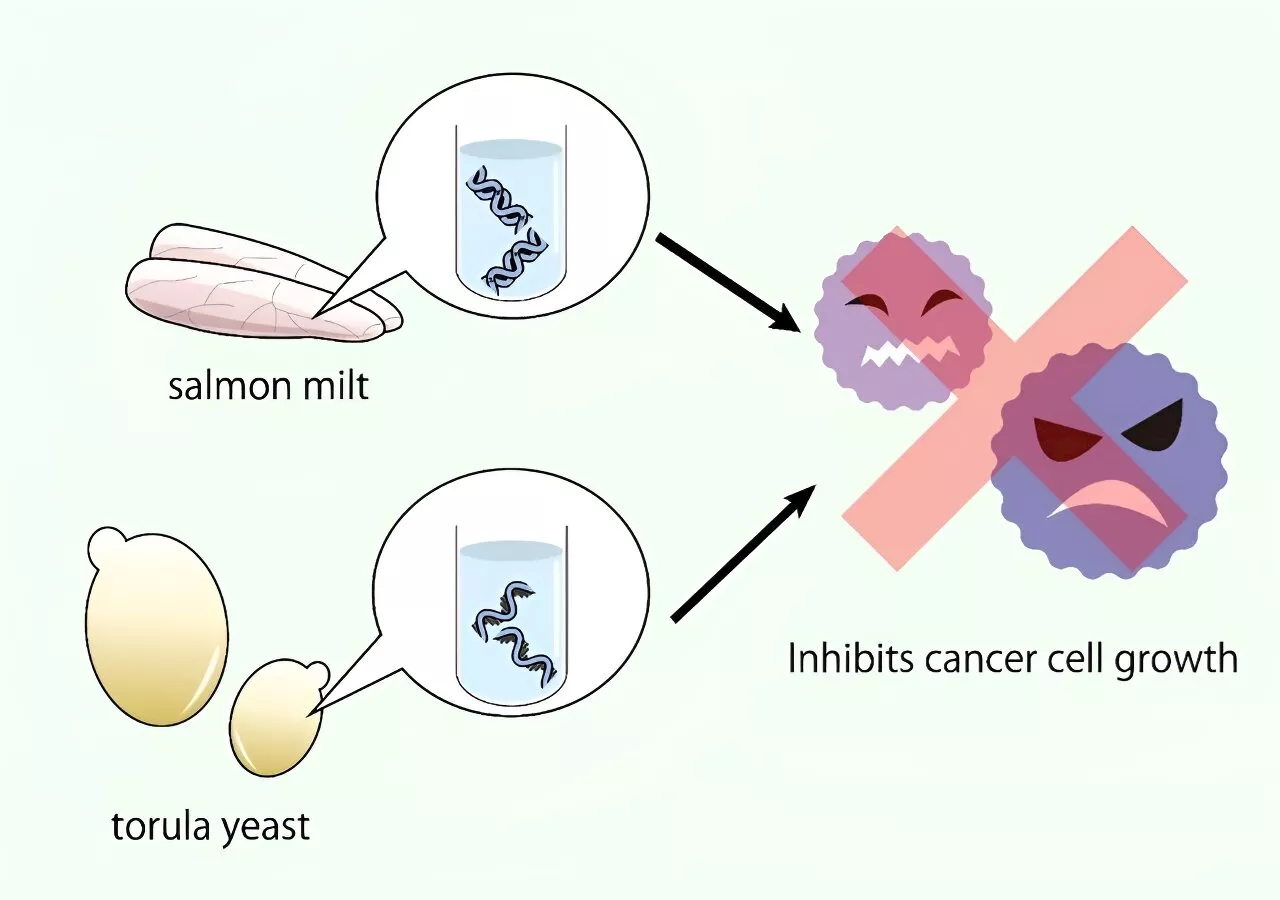
When people eat, they ingest the nucleic acids that reside in all living things. The compounds in these acids could inhibit the growth of cancer cells, according to findings published in PLOS ONE by Osaka Metropolitan University Associate Professor Akiko Kojima-Yuasa of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology and colleagues.
Compounds from nucleic acids in food show anticancer effects retrieved 29 August 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-08-compounds-nucleic-acids-food-anticancer.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Protect your teeth with fruit: antimicrobial effects found in biomass compoundsA research team has verified the antibacterial effect of seven food-derived flavonoids against periodontal pathogenic bacteria. The results showed that though several of the compounds inhibited bacterial growth, Pru-C12 had the highest antimicrobial effect.
Protect your teeth with fruit: antimicrobial effects found in biomass compoundsA research team has verified the antibacterial effect of seven food-derived flavonoids against periodontal pathogenic bacteria. The results showed that though several of the compounds inhibited bacterial growth, Pru-C12 had the highest antimicrobial effect.
Read more »
 New UVA study identifies promising drugs to regenerate heart tissue post-attackUVA researchers make a breakthrough in heart regeneration by identifying compounds that stimulate cardiomyocyte production.
New UVA study identifies promising drugs to regenerate heart tissue post-attackUVA researchers make a breakthrough in heart regeneration by identifying compounds that stimulate cardiomyocyte production.
Read more »
 Breakthrough in Z-alkene synthesis: Scientists develop efficient and sustainable methodZ-alkenes are organic compounds with a double bond between two carbon atoms and two substituents attached to the carbon atoms on the same side of the double bond. They are ubiquitous structural components of organic compounds in chemistry and biology.
Breakthrough in Z-alkene synthesis: Scientists develop efficient and sustainable methodZ-alkenes are organic compounds with a double bond between two carbon atoms and two substituents attached to the carbon atoms on the same side of the double bond. They are ubiquitous structural components of organic compounds in chemistry and biology.
Read more »
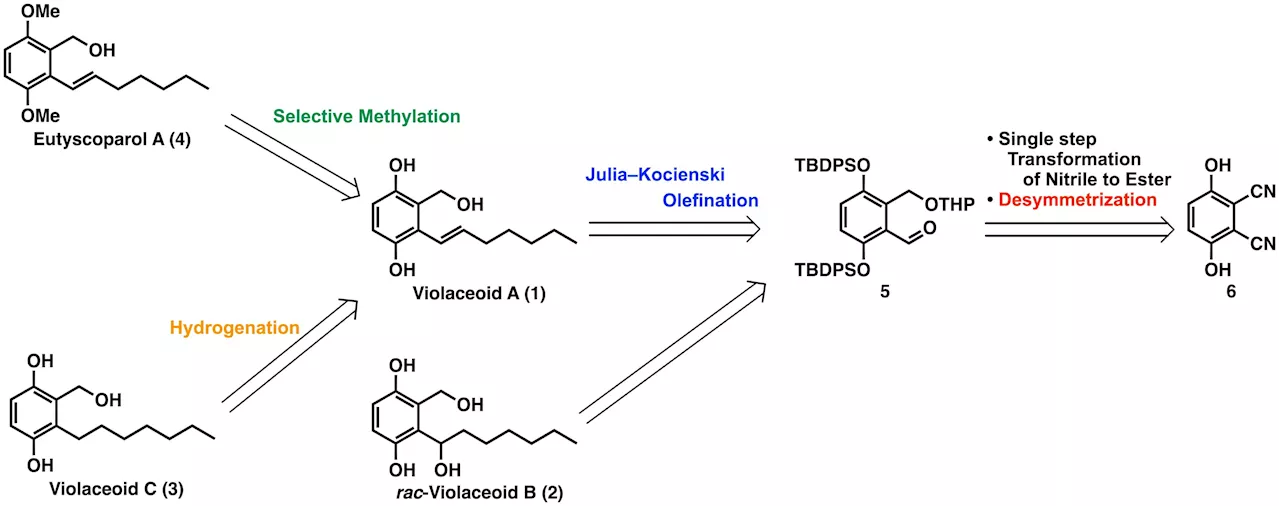 From fungi to pharmaceuticals: A milestone for the production of eutyscoparol A and violaceoid CThe natural world is rich in chemical compounds with remarkable medicinal properties. A notable example is penicillin, discovered by chance from the Penicillium mold. This discovery revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections and highlighted the potential of natural compounds in medicine.
From fungi to pharmaceuticals: A milestone for the production of eutyscoparol A and violaceoid CThe natural world is rich in chemical compounds with remarkable medicinal properties. A notable example is penicillin, discovered by chance from the Penicillium mold. This discovery revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections and highlighted the potential of natural compounds in medicine.
Read more »
 Massachusetts governor signs law phasing out toxic PFAS in firefighters' gearMassachusetts Gov. Maura Healey signed into law Thursday a bill that would phase out the use of PFAS, a group of toxic industrial compounds, in firefighters' protective gear.
Massachusetts governor signs law phasing out toxic PFAS in firefighters' gearMassachusetts Gov. Maura Healey signed into law Thursday a bill that would phase out the use of PFAS, a group of toxic industrial compounds, in firefighters' protective gear.
Read more »
 Forever chemical pollution can now be trackedResearchers developed a way to fingerprint organofluorine compounds -- sometimes called 'forever chemicals' --which could help authorities trace them to their source when they end up in aquifers, waterways or soil.
Forever chemical pollution can now be trackedResearchers developed a way to fingerprint organofluorine compounds -- sometimes called 'forever chemicals' --which could help authorities trace them to their source when they end up in aquifers, waterways or soil.
Read more »