A study in BMCMedicine demonstrates that adhesion molecule TMIGD1 is negatively associated with inflammatory characteristics of Crohn’s disease and can be a potential therapeutic target for it.
]. Adenoviruses for Tmigd1 and Banf1 overexpression and control viruses were administered to mice by intraperitoneal injection.Caco2, a colonic epithelial adenocarcinoma cell line, was purchased from the American Tissue Culture Collection and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% antibiotics .
For mice, 4 kD fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran powder was dissolved in PBS to obtain an 80 mg/mL solution. Mice were fasted for 4 h prior to gavage with 150 μL of FD4 solution. Three hours after gavage, the mice were anesthetized and their blood was collected and kept in the dark. The leakage of FD4 into the circulation was determined by measuring serum fluorescence . For cells, FD4 powder was dissolved in Opti-MEM to obtain a 2 mg/mL solution.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 The secular trend of enterovirus A71 after the implementation of preventive measures in Taiwan - BMC Public HealthBackground Enterovirus A71 (EV A71) is one of the most important enteroviruses related to morbidity and mortality in children worldwide. This study aimed to analyse the secular trend of EV A71 in Taiwan from 1998 to 2020 and to evaluate the effectiveness of infection control measures. Methods We collected the epidemiological data of EV A71 from disease surveillance systems in Taiwan. We analysed the association between the secular trend of EV A71 and preventive measures such as hand washing, case isolation, and suspension of classes. Results The incidence of enterovirus infections with severe complications (EVSC) decreased from 16.25 per 100,000 children under six in 1998 to less than 9.73 per 100,000 children under six after 2012 (P = 0.0022). The mortality rate also decreased significantly, from 3.52 per 100,000 children under six in 1998 to 0 per 100,000 children under six in 2020 (P | 0.0001). The numbers of EVSC and fatalities were significantly higher in the years when EV A71 accounted for more than 10% of the annual predominant serotypes (p | 0.05). After the implementation of many non-pharmaceutical interventions in 2012, the incidence of EVSC and mortality rate decreased significantly (p | 0.001). Conclusions After implementing active enterovirus surveillance and preventive measures, we found that the incidence of EVSC and fatalities due to EV A71 in Taiwan decreased significantly from 1998 to 2020. Continuous surveillance and strengthened infection control policies are still needed in the future.
The secular trend of enterovirus A71 after the implementation of preventive measures in Taiwan - BMC Public HealthBackground Enterovirus A71 (EV A71) is one of the most important enteroviruses related to morbidity and mortality in children worldwide. This study aimed to analyse the secular trend of EV A71 in Taiwan from 1998 to 2020 and to evaluate the effectiveness of infection control measures. Methods We collected the epidemiological data of EV A71 from disease surveillance systems in Taiwan. We analysed the association between the secular trend of EV A71 and preventive measures such as hand washing, case isolation, and suspension of classes. Results The incidence of enterovirus infections with severe complications (EVSC) decreased from 16.25 per 100,000 children under six in 1998 to less than 9.73 per 100,000 children under six after 2012 (P = 0.0022). The mortality rate also decreased significantly, from 3.52 per 100,000 children under six in 1998 to 0 per 100,000 children under six in 2020 (P | 0.0001). The numbers of EVSC and fatalities were significantly higher in the years when EV A71 accounted for more than 10% of the annual predominant serotypes (p | 0.05). After the implementation of many non-pharmaceutical interventions in 2012, the incidence of EVSC and mortality rate decreased significantly (p | 0.001). Conclusions After implementing active enterovirus surveillance and preventive measures, we found that the incidence of EVSC and fatalities due to EV A71 in Taiwan decreased significantly from 1998 to 2020. Continuous surveillance and strengthened infection control policies are still needed in the future.
Read more »
 Cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton) Seeds Intake Increases Energy Expenditure and Reduces Fat Mass in Mice by Modulating Neural Circuits That Regulate Adipose Tissue Lipolysis and Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism in Liver and Skeletal MuscleCardamom seed (Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton; EC) is consumed in several countries worldwide and is considered a nutraceutical spice since it exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic activities. In obese individuals, EC intake also favors weight loss. However, the mechanism for these effects has not been studied. Here, we identified that EC modulates the neuroendocrine axis that regulates food intake, body weight, mitochondrial activity, and energy expenditure in mice. We fed C57BL/6 mice with diets containing 3%, 6%, or 12% EC or a control diet for 14 weeks. Mice fed the EC-containing diets gained less weight than control, despite slightly higher food intake. The lower final weight of EC-fed mice was due to lesser fat content but increased lean mass than control. EC intake increased lipolysis in subcutaneous adipose tissue, and reduced adipocyte size in subcutaneous, visceral, and brown adipose tissues. EC intake also prevented lipid droplet accumulation and increased mitochondrial content in skeletal muscle and liver. Accordingly, fasting and postprandial oxygen consumption, as well as fasting fat oxidation and postprandial glucose utilization were higher in mice fed with EC than in control. EC intake reduced proopiomelanocortin (POMC) mRNA content in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, without an impact on neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA. These neuropeptides control food intake but also influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axes. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) mRNA expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and circulating triiodothyronine (T3) were lower in EC-fed mice than in control. This effect was linked with decreased circulating corticosterone and weight of adrenal glands. Our results indicate that EC modulates appetite, increases lipolysis in adipose tissue and mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in liver and skeletal muscle, leading to increased energy expenditure and lower
Cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton) Seeds Intake Increases Energy Expenditure and Reduces Fat Mass in Mice by Modulating Neural Circuits That Regulate Adipose Tissue Lipolysis and Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism in Liver and Skeletal MuscleCardamom seed (Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton; EC) is consumed in several countries worldwide and is considered a nutraceutical spice since it exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic activities. In obese individuals, EC intake also favors weight loss. However, the mechanism for these effects has not been studied. Here, we identified that EC modulates the neuroendocrine axis that regulates food intake, body weight, mitochondrial activity, and energy expenditure in mice. We fed C57BL/6 mice with diets containing 3%, 6%, or 12% EC or a control diet for 14 weeks. Mice fed the EC-containing diets gained less weight than control, despite slightly higher food intake. The lower final weight of EC-fed mice was due to lesser fat content but increased lean mass than control. EC intake increased lipolysis in subcutaneous adipose tissue, and reduced adipocyte size in subcutaneous, visceral, and brown adipose tissues. EC intake also prevented lipid droplet accumulation and increased mitochondrial content in skeletal muscle and liver. Accordingly, fasting and postprandial oxygen consumption, as well as fasting fat oxidation and postprandial glucose utilization were higher in mice fed with EC than in control. EC intake reduced proopiomelanocortin (POMC) mRNA content in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, without an impact on neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA. These neuropeptides control food intake but also influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axes. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) mRNA expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and circulating triiodothyronine (T3) were lower in EC-fed mice than in control. This effect was linked with decreased circulating corticosterone and weight of adrenal glands. Our results indicate that EC modulates appetite, increases lipolysis in adipose tissue and mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in liver and skeletal muscle, leading to increased energy expenditure and lower
Read more »
 Luke Brooks: State of mouldy home did not cause death - inquestDamp, mould and leaks were found in Luke Brooks' home before he died of respiratory disease.
Luke Brooks: State of mouldy home did not cause death - inquestDamp, mould and leaks were found in Luke Brooks' home before he died of respiratory disease.
Read more »
 Asylum seekers evacuate barge after Legionella bacteria found in water supplyAsylum seekers have been forced to evacuate from the Bibby Stockholm barge in Dorset after traces of Legionella bacteria, which can cause Legionnaires disease, were found in the water supply.
Asylum seekers evacuate barge after Legionella bacteria found in water supplyAsylum seekers have been forced to evacuate from the Bibby Stockholm barge in Dorset after traces of Legionella bacteria, which can cause Legionnaires disease, were found in the water supply.
Read more »
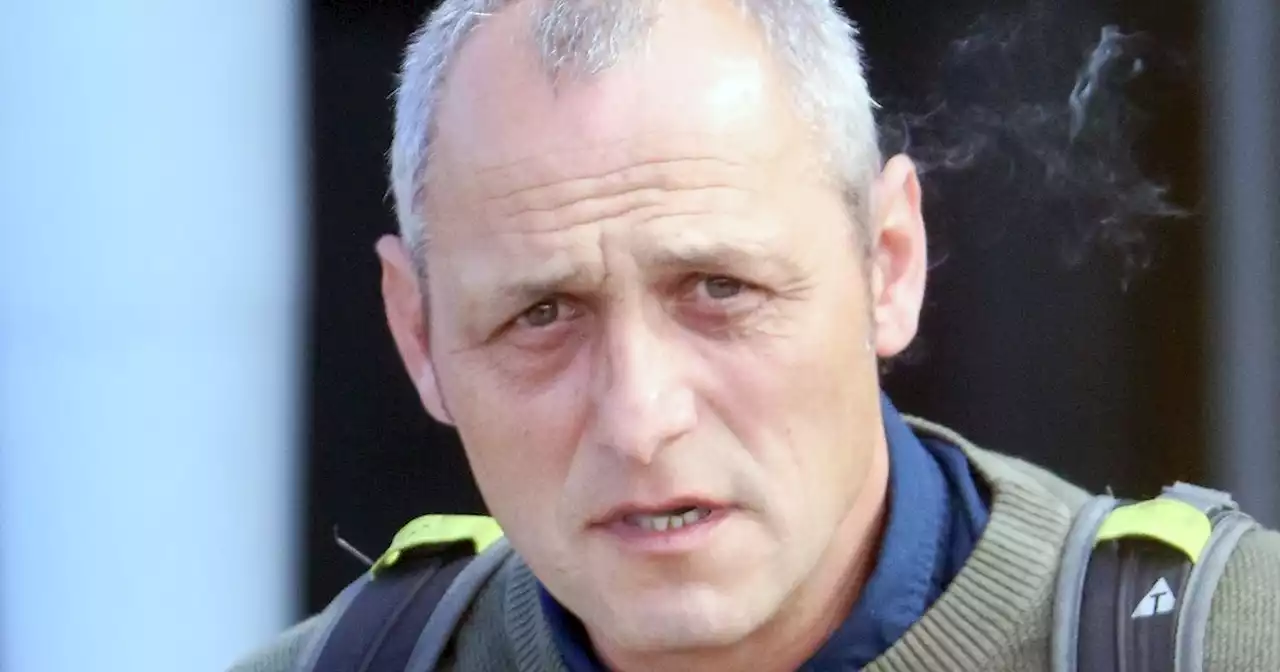 Drunk truck driver on M8 smashed into Tesco barrier causing £3k damage to lorryArmy veteran Peter Tuck was driving dangerously along the busy motorway when concerned motorists got in touch with his bosses before he pulled over at Harthill services.
Drunk truck driver on M8 smashed into Tesco barrier causing £3k damage to lorryArmy veteran Peter Tuck was driving dangerously along the busy motorway when concerned motorists got in touch with his bosses before he pulled over at Harthill services.
Read more »
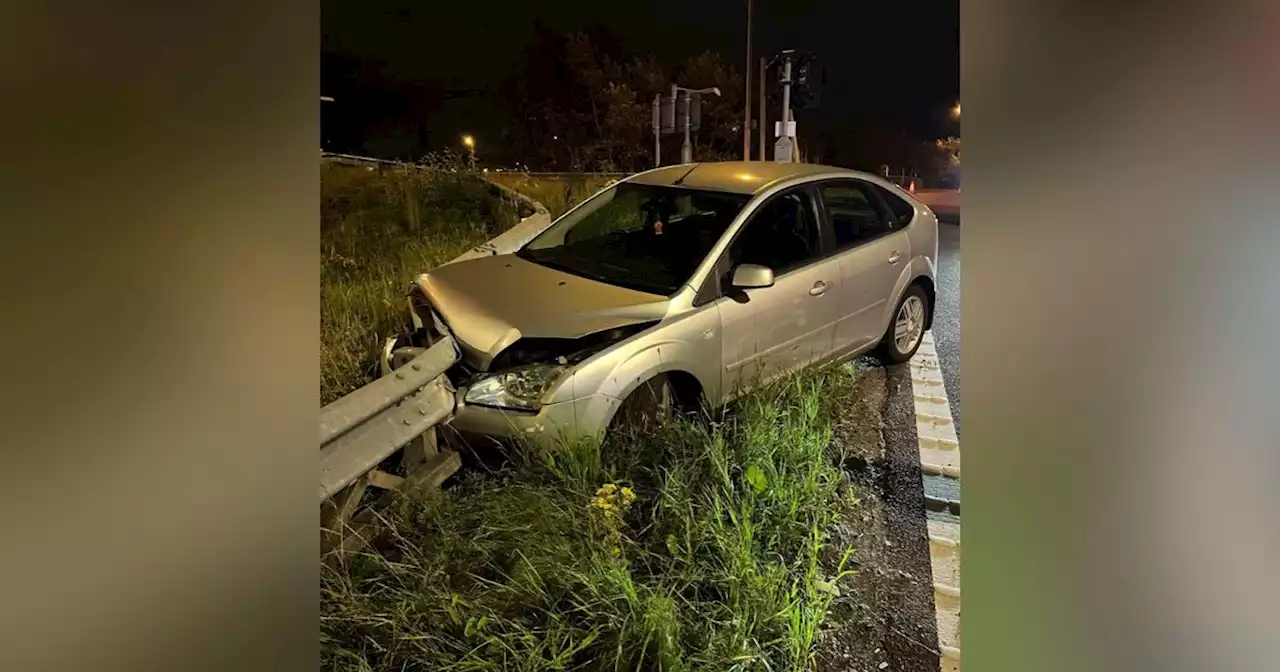 Wrecked car seized after being ploughed into metal barrier by 'drink driver'Wrecked car seized by police after being ploughed into metal barrier by suspected drink driver
Wrecked car seized after being ploughed into metal barrier by 'drink driver'Wrecked car seized by police after being ploughed into metal barrier by suspected drink driver
Read more »
