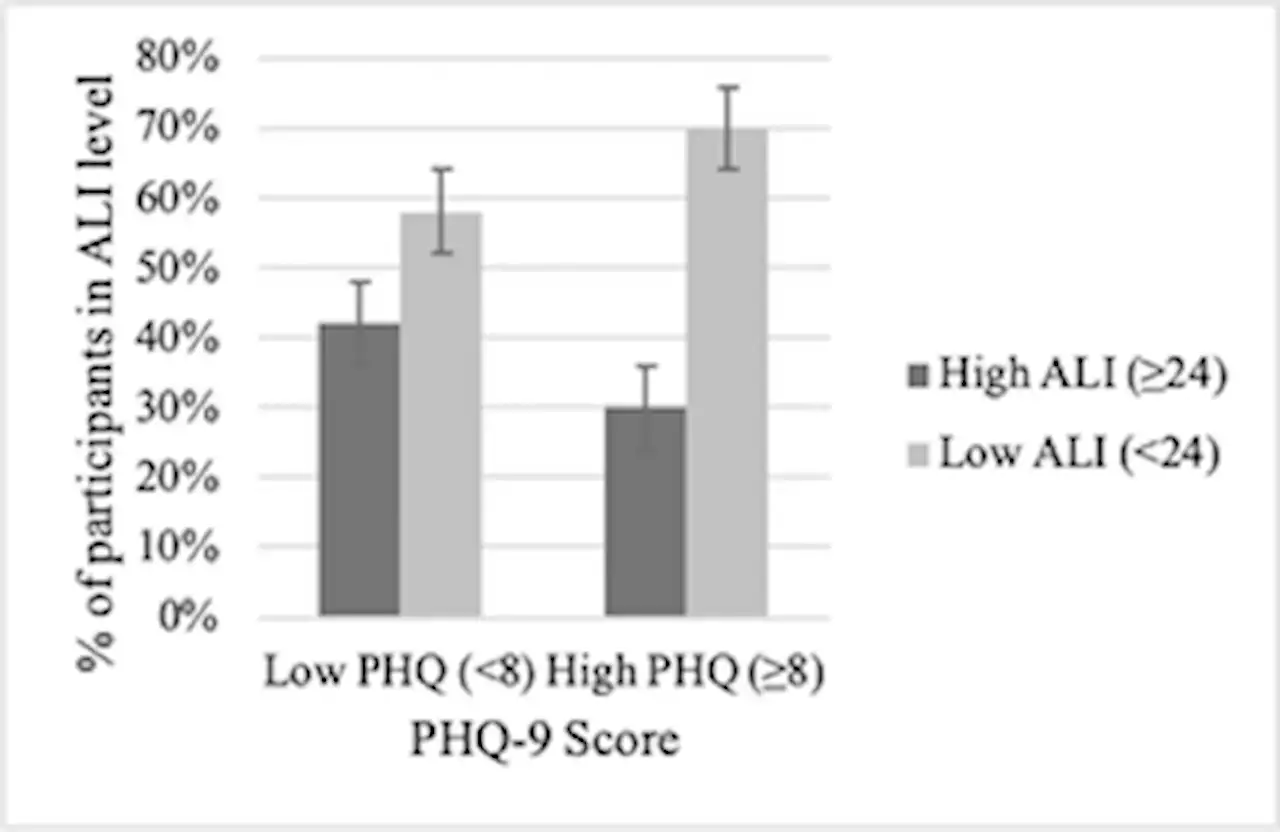
Depression linked to deadly inflammation in lungcancer patients OhioState PLOSONE
Contributed equally to this work with: Barbara L. Andersen, John Myers, Peter G. Shields, William E.
CarsonConceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editingDepartment of Psychology, Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, United States of America
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Systemic GDF11 attenuates depression-like phenotype in aged mice via stimulation of neuronal autophagy - Nature AgingMoigneu, Abdellaoui and colleagues show that GDF11 attenuates depression-like behavior and improves memory in aged mice through neuronal autophagy and mTOR. Serum levels of GDF11 are inversely associated with depression in patients.
Systemic GDF11 attenuates depression-like phenotype in aged mice via stimulation of neuronal autophagy - Nature AgingMoigneu, Abdellaoui and colleagues show that GDF11 attenuates depression-like behavior and improves memory in aged mice through neuronal autophagy and mTOR. Serum levels of GDF11 are inversely associated with depression in patients.
Read more »
 ‘Just snap out of it’ – the experience of loneliness in women with perinatal depression: a Meta-synthesis of qualitative studies - BMC PsychiatryBackground Pregnancy and the arrival of a new baby is a time of great transition and upheaval. Women often experience social isolation and loneliness at this time and may develop depression, particularly in the postnatal period. Qualitative studies have reported that loneliness is also a feature of perinatal depression. However, until now there has been no attempt to synthesise research exploring the links between loneliness and perinatal depression. This study’s aim was to explore existing qualitative evidence to answer two research questions: What are the experiences of loneliness for women with perinatal depression? What helps and what makes loneliness worse for women with perinatal depression? Methods A qualitative meta-synthesis retrieved primary qualitative studies relevant to the research questions. Four electronic databases were systematically searched (Ovid MEDLINE®; PsycINFO; Embase; Web of Science). Papers were screened according to pre-defined inclusion criteria and assigned a quality score. Thematic analysis was used to identify major overarching themes in the literature. Results Twenty-seven relevant qualitative studies were included. Themes relating to the interaction between perinatal depression and loneliness included self-isolation and hiding symptoms due to stigma of perinatal depression and fear of judgement as a ‘bad mother’; a sudden sense of emotional disconnection after birth; and a mismatch between expected and actual support provided by partner, family and community. There was also a double burden of loneliness for women from disadvantaged communities, due to increased stigma and decreased social support. Validation and understanding from healthcare professionals, peer support from other mothers with experience of perinatal depression, and practical and emotional family support were all important factors that could ameliorate loneliness. Conclusions Loneliness appears to play a central role in the experience of perinatal depression based on
‘Just snap out of it’ – the experience of loneliness in women with perinatal depression: a Meta-synthesis of qualitative studies - BMC PsychiatryBackground Pregnancy and the arrival of a new baby is a time of great transition and upheaval. Women often experience social isolation and loneliness at this time and may develop depression, particularly in the postnatal period. Qualitative studies have reported that loneliness is also a feature of perinatal depression. However, until now there has been no attempt to synthesise research exploring the links between loneliness and perinatal depression. This study’s aim was to explore existing qualitative evidence to answer two research questions: What are the experiences of loneliness for women with perinatal depression? What helps and what makes loneliness worse for women with perinatal depression? Methods A qualitative meta-synthesis retrieved primary qualitative studies relevant to the research questions. Four electronic databases were systematically searched (Ovid MEDLINE®; PsycINFO; Embase; Web of Science). Papers were screened according to pre-defined inclusion criteria and assigned a quality score. Thematic analysis was used to identify major overarching themes in the literature. Results Twenty-seven relevant qualitative studies were included. Themes relating to the interaction between perinatal depression and loneliness included self-isolation and hiding symptoms due to stigma of perinatal depression and fear of judgement as a ‘bad mother’; a sudden sense of emotional disconnection after birth; and a mismatch between expected and actual support provided by partner, family and community. There was also a double burden of loneliness for women from disadvantaged communities, due to increased stigma and decreased social support. Validation and understanding from healthcare professionals, peer support from other mothers with experience of perinatal depression, and practical and emotional family support were all important factors that could ameliorate loneliness. Conclusions Loneliness appears to play a central role in the experience of perinatal depression based on
Read more »
 Jonnie Irwin returns to A Place In The Sun amid terminal lung cancer battleTV presenter Jonnie Irwin made a return to A Place In The Sun as he put in an appearance at a live show in Manchester amid his battle with terminal lung cancer
Jonnie Irwin returns to A Place In The Sun amid terminal lung cancer battleTV presenter Jonnie Irwin made a return to A Place In The Sun as he put in an appearance at a live show in Manchester amid his battle with terminal lung cancer
Read more »
 Harassment of Hong Kong expats proves the Government is weak on China, says Iain Duncan SmithSenior backbench Tory MP Sir Iain Duncan Smith has called on the Government to “wake up” to the systemic threat of China after theipaper revealed Hong Kong dissidents who have fled to the UK been followed and harassed by suspected pro-Beijing informants
Harassment of Hong Kong expats proves the Government is weak on China, says Iain Duncan SmithSenior backbench Tory MP Sir Iain Duncan Smith has called on the Government to “wake up” to the systemic threat of China after theipaper revealed Hong Kong dissidents who have fled to the UK been followed and harassed by suspected pro-Beijing informants
Read more »
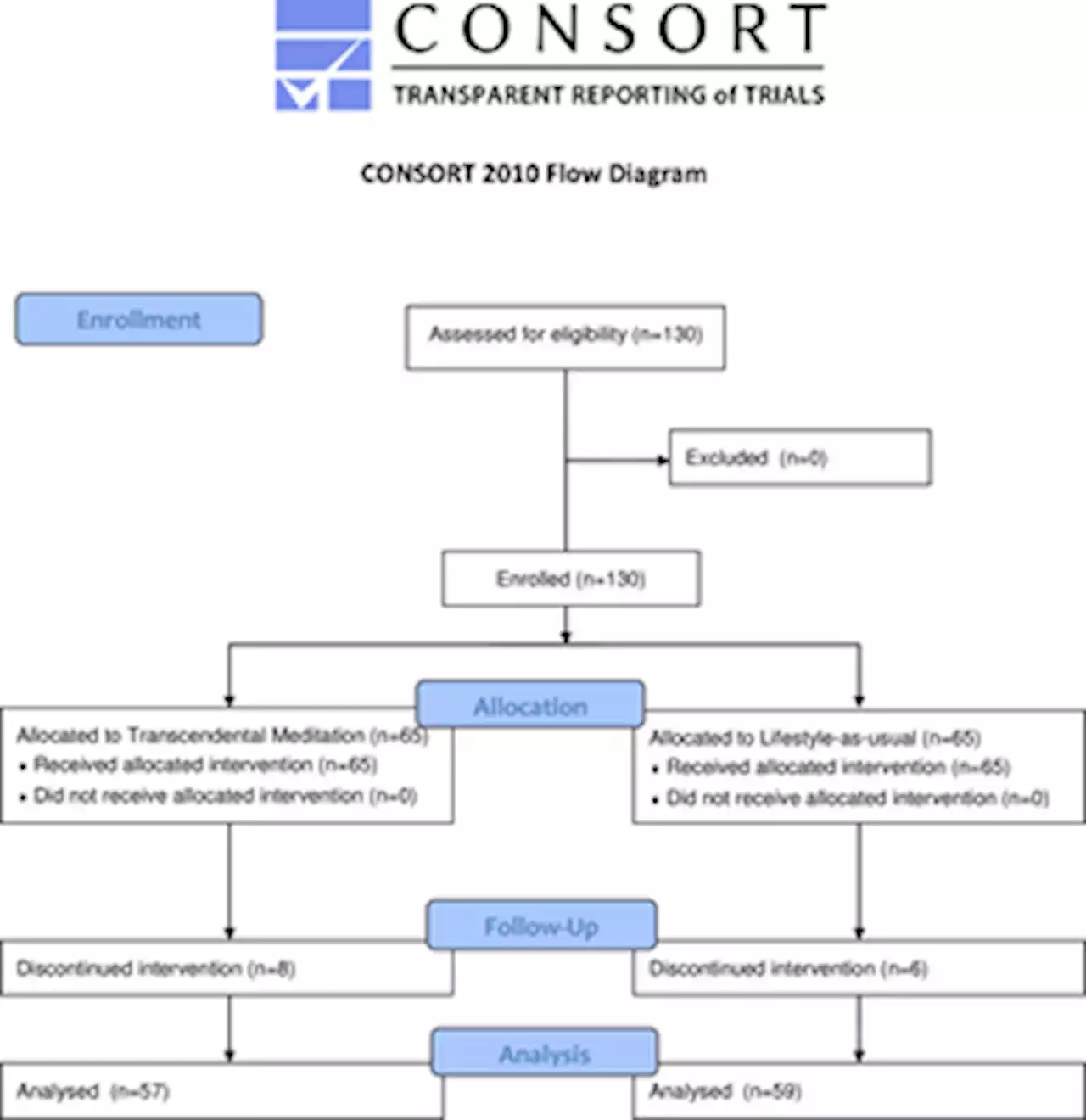 Improving the mental health and well-being of healthcare providers using the transcendental meditation technique during the COVID-19 pandemic: A parallel population studyIntroduction Frontline Healthcare provider (HCP) burnout has dramatically increased due to the COVID 19 pandemic. Hospitals are supporting wellness programs and techniques to reduce burnout including the Transcendental Meditation (TM) technique. This study evaluated the use of TM on HCP symptoms of stress, burnout and wellness. Methods A total of 65 HCPs at three South Florida hospitals were recruited and instructed in the TM technique which they practiced at home for 20 minutes twice a day. A parallel lifestyle as usual control group was enrolled. Validated measurement scales (Brief Symptom Inventory 18 (BSI-18), Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), Maslach Burnout Inventory-Human Services Survey [MBI-HSS (MP)] and the Warwick Edinburgh Mental Well Being Scale (WEMWBS) were administered at baseline, 2 weeks, one and three months. Results No significant demographic differences were seen between the 2 groups; however, some baseline scales were higher in the TM group. TM average weekly session completion rate was very high at 83%. After 2-weeks, symptoms of somatization, depression, and anxiety in the TM group had all shown near 45% reductions, while insomnia, emotional exhaustion, and well-being had improved by 33%, 16%, and 11% respectively (P=0.02 for somatization and | .001 for all others); no significant change was noted in the LAU group. At 3-months, in the TM group, the improvement in symptoms showed a mean reduction of in anxiety, 62%, somatization, 58%, depression, 50%, insomnia, 44%, emotional exhaustion 40%, depersonalization, 42%, and improvement of well-being 18% (for all p|0.004). P-values for between-group differences in change from baseline, based upon repeated measures ANCOVA covarying for baseline measurements, showed significance for all scales at 3-months. Conclusion The study confirmed the reported significant and rapid benefits of the practice of TM and demonstrated its positive psychological impact on healthcare workers in a high stress setting.
Improving the mental health and well-being of healthcare providers using the transcendental meditation technique during the COVID-19 pandemic: A parallel population studyIntroduction Frontline Healthcare provider (HCP) burnout has dramatically increased due to the COVID 19 pandemic. Hospitals are supporting wellness programs and techniques to reduce burnout including the Transcendental Meditation (TM) technique. This study evaluated the use of TM on HCP symptoms of stress, burnout and wellness. Methods A total of 65 HCPs at three South Florida hospitals were recruited and instructed in the TM technique which they practiced at home for 20 minutes twice a day. A parallel lifestyle as usual control group was enrolled. Validated measurement scales (Brief Symptom Inventory 18 (BSI-18), Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), Maslach Burnout Inventory-Human Services Survey [MBI-HSS (MP)] and the Warwick Edinburgh Mental Well Being Scale (WEMWBS) were administered at baseline, 2 weeks, one and three months. Results No significant demographic differences were seen between the 2 groups; however, some baseline scales were higher in the TM group. TM average weekly session completion rate was very high at 83%. After 2-weeks, symptoms of somatization, depression, and anxiety in the TM group had all shown near 45% reductions, while insomnia, emotional exhaustion, and well-being had improved by 33%, 16%, and 11% respectively (P=0.02 for somatization and | .001 for all others); no significant change was noted in the LAU group. At 3-months, in the TM group, the improvement in symptoms showed a mean reduction of in anxiety, 62%, somatization, 58%, depression, 50%, insomnia, 44%, emotional exhaustion 40%, depersonalization, 42%, and improvement of well-being 18% (for all p|0.004). P-values for between-group differences in change from baseline, based upon repeated measures ANCOVA covarying for baseline measurements, showed significance for all scales at 3-months. Conclusion The study confirmed the reported significant and rapid benefits of the practice of TM and demonstrated its positive psychological impact on healthcare workers in a high stress setting.
Read more »
 Researchers optically evoke tachycardia enhanced anxiety-like behaviourIn a recent study published in the journal Nature, researchers devised a non-invasive optogenetic and wearable cardiac pacemaker for accurate and specific control of cardiac rhythm for ≤900 beats per minute (bpm), enabled by micro-light-emitting display (LED) harness and systemic channelrhodopsin delivery.
Researchers optically evoke tachycardia enhanced anxiety-like behaviourIn a recent study published in the journal Nature, researchers devised a non-invasive optogenetic and wearable cardiac pacemaker for accurate and specific control of cardiac rhythm for ≤900 beats per minute (bpm), enabled by micro-light-emitting display (LED) harness and systemic channelrhodopsin delivery.
Read more »