A new study from the University of Copenhagen reveals that genetic factors contributing to smoking and high body mass index (BMI) are significantly associated with an increased risk of dementia. Conversely, education and physical activity appear to offer protective benefits.
By Hugo Francisco de SouzaReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.Oct 17 2024 New research from the University of Copenhagen links genetic predispositions to smoking and high BMI with elevated dementia risk while highlighting the protective power of education and physical activity.
Triglycerides as a key risk factor: The study identified high triglycerides, often overlooked in dementia research, as significantly increasing the risk of all-cause and vascular dementia. Background Dementia is a serious and potentially lethal age-associated neurological condition characterized by a substantial gradual decline in cognitive functions such as memory, thinking, and judgment. It is one of the most prevalent causes of non-communicable disability and death and, unfortunately, remains without cure.
Despite decades of research, causal associations between modifiable risk factors and dementia outcomes remain vague and often confounding. Studies have attempted to elucidate the mechanisms underpinning these associations, but the current lack of discrete-age datasets and analyses leads to several studies, even using identical datasets, providing contrasting outcomes.
No evidence of alcohol impact: Unlike other risk factors, the study found no significant genetic association between alcohol consumption and dementia, despite prior observational studies suggesting otherwise. GWAS MR predictions revealed that of the 14 factors listed in the Lancet Commission report, genetic predispositions to high BMI resulted in dementia most frequently. Similarly, frequent smoking , high systolic and diastolic blood pressure , high LDL cholesterol , high triglycerides , and T2D substantially increased future dementia risk.
DEMETIA RISK GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONS SMOKING BMI EDUCATION PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
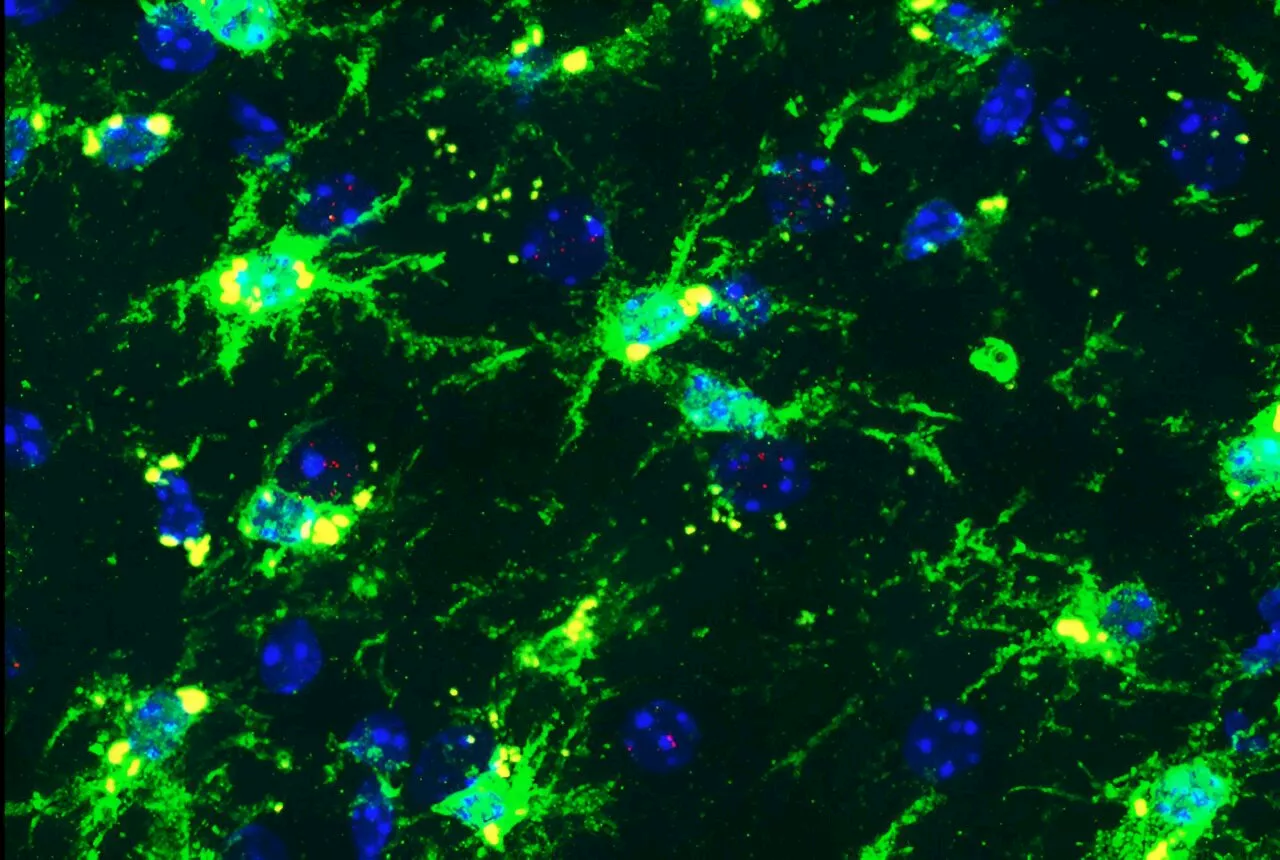 Genetic variants linked to Alzheimer's trigger brain inflammation in females, preclinical study findsWeill Cornell Medicine investigators have found that two genetic variants that confer high risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD) together trigger a harmful inflammatory response in the brain's immune cells, particularly in females, in a preclinical model.
Genetic variants linked to Alzheimer's trigger brain inflammation in females, preclinical study findsWeill Cornell Medicine investigators have found that two genetic variants that confer high risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD) together trigger a harmful inflammatory response in the brain's immune cells, particularly in females, in a preclinical model.
Read more »
 Study reveals genetic elements driving Klebsiella pneumoniae hypervirulenceMore than a decade ago, physicians around the world began reporting cases due to a new hypervirulent strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae, which could infect and severely sicken otherwise healthy people.
Study reveals genetic elements driving Klebsiella pneumoniae hypervirulenceMore than a decade ago, physicians around the world began reporting cases due to a new hypervirulent strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae, which could infect and severely sicken otherwise healthy people.
Read more »
 Genetic study uncovers key drivers of metabolic syndrome with brain tissue linksResearchers uncovered 1,307 genetic loci linked to metabolic syndrome, revealing brain tissue enrichment and key genetic factors in its development. The study also shows polygenic risk scores predict metabolic syndrome across populations.
Genetic study uncovers key drivers of metabolic syndrome with brain tissue linksResearchers uncovered 1,307 genetic loci linked to metabolic syndrome, revealing brain tissue enrichment and key genetic factors in its development. The study also shows polygenic risk scores predict metabolic syndrome across populations.
Read more »
 Study uncovers novel genetic variant associated with intellectual disabilityResearchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have published a pivotal study in Nature Genetics (DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01917-1) that sheds light on a novel genetic variant associated with intellectual capacities and educational outcomes.
Study uncovers novel genetic variant associated with intellectual disabilityResearchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have published a pivotal study in Nature Genetics (DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01917-1) that sheds light on a novel genetic variant associated with intellectual capacities and educational outcomes.
Read more »
 Study uncovers genetic changes linked to leukemia risk in people with Down's syndromePeople with Down's syndrome face a higher risk of developing Leukemia. Now researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Stanford University explain why, by identifying specific changes in blood cells of people with Down's syndrome.
Study uncovers genetic changes linked to leukemia risk in people with Down's syndromePeople with Down's syndrome face a higher risk of developing Leukemia. Now researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Stanford University explain why, by identifying specific changes in blood cells of people with Down's syndrome.
Read more »
 Study highlights gender differences in genetic risk for psychotic disordersA team of researchers from the University of Barcelona and the Centre for Biomedical Research in the Mental Health Network (CIBERSAM) has published a pioneering study that reveals significant findings in the field of genetic psychiatry from the perspective of separate gender analysis.
Study highlights gender differences in genetic risk for psychotic disordersA team of researchers from the University of Barcelona and the Centre for Biomedical Research in the Mental Health Network (CIBERSAM) has published a pioneering study that reveals significant findings in the field of genetic psychiatry from the perspective of separate gender analysis.
Read more »
