Researchers assess the association between erectile dysfunction and the Compound Dietary Antioxidant Index.
By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc.Sep 16 2024 New study links higher antioxidant intake to reduced erectile dysfunction risk, highlighting the potential role of diet in ED prevention. Study: Association between composite dietary antioxidant index and erectile dysfunction among American adults: a cross sectional study. Image Credit: R Photography Background / Shutterstock.
Molecular inflammation and oxidative stress play a key role in ED pathophysiological mechanisms. The accumulation of reactive oxygen species leads to oxidative stress, which can precipitate vascular endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Individuals with a prostate cancer diagnosis and those lacking data on dietary antioxidants, body mass index , smoking or alcohol use, marital status, level of education, cardiovascular disease, recreational activity, and hypertension were excluded from the study.
Men with ED were typically in a marriage or cohabitating, older, had greater BMI values, possessed a higher level of education, engaged in less physical activity, and consumed alcohol. ED patients were also more likely to be diagnosed with hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease , and hypercholesterolemia.
The dose-dependent relationship between CDAI and ED was examined using restricted cubic splines . Herein, a non-linear and negative association was observed, in which the risk of ED declined sharply with initial increases in CDAI scores until ultimately reaching a plateau.
Alcohol Antioxidant Atherosclerosis Blood Blood Pressure Cardiovascular Disease Compound Coronary Artery Disease Diabetes Education Exercise High Blood Pressure Hypercholesterolemia Inflammation Nutrition Oxidative Stress Smoking Stress
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
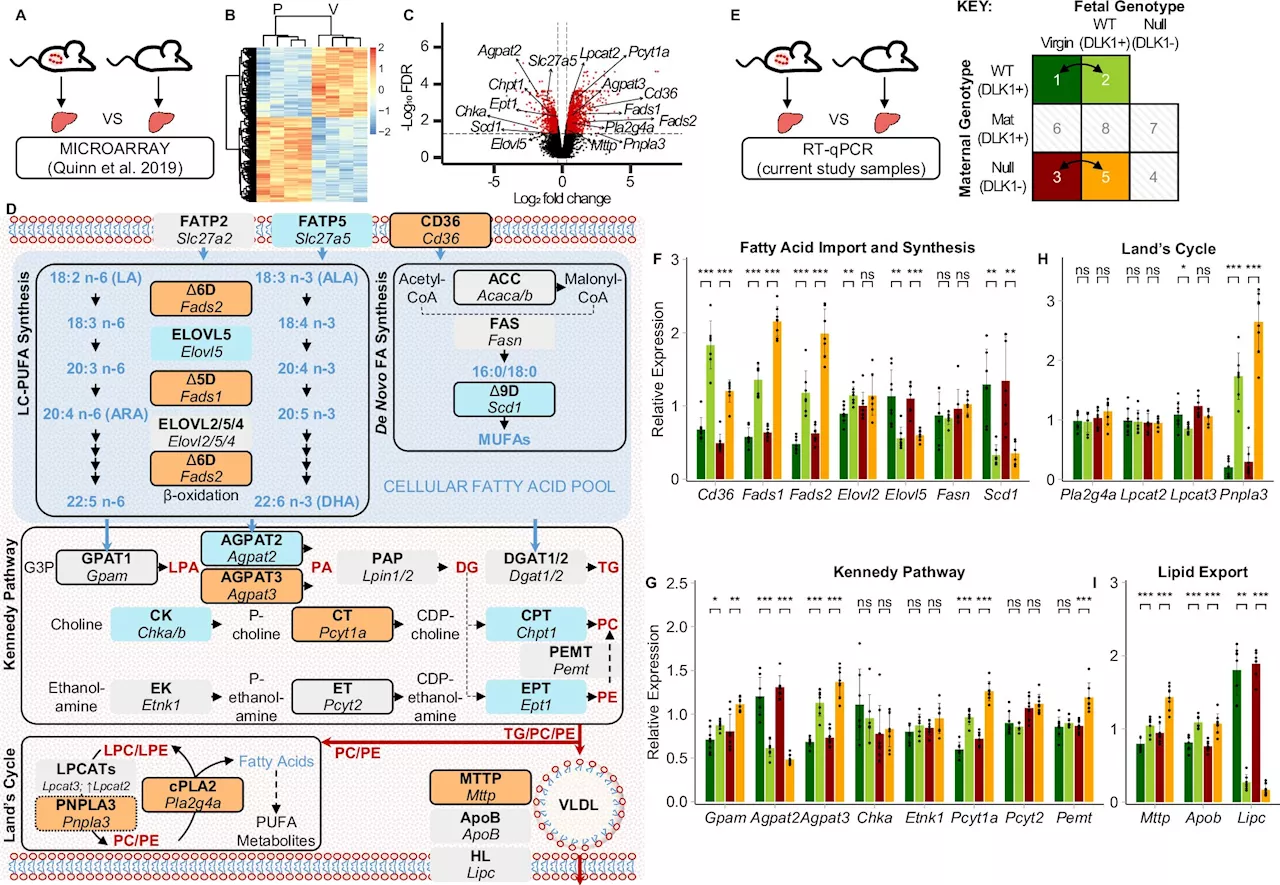 Researchers identify molecular mechanism that transports important dietary fats to the fetusResearch in mouse models has identified a new mechanism for how long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFAs), like omega-3s, are transported from the mother to the fetus during pregnancy. The results, published in Nature Communications, could help to identify ways to tackle LC-PUFA deficiency in the developing fetus.
Researchers identify molecular mechanism that transports important dietary fats to the fetusResearch in mouse models has identified a new mechanism for how long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFAs), like omega-3s, are transported from the mother to the fetus during pregnancy. The results, published in Nature Communications, could help to identify ways to tackle LC-PUFA deficiency in the developing fetus.
Read more »
 Researchers develop stable compound for targeted alpha therapy in prostate cancerCompounds containing astatine-211 (211At) can be used in targeted radiotherapies for prostate cancer, but deastatination in the body remains a significant hurdle.
Researchers develop stable compound for targeted alpha therapy in prostate cancerCompounds containing astatine-211 (211At) can be used in targeted radiotherapies for prostate cancer, but deastatination in the body remains a significant hurdle.
Read more »
 High-protein diets: How they affect weight, energy, and blood sugar levelsResearchers review the effects of dietary protein on energy intake, appetite, and postprandial glycemia.
High-protein diets: How they affect weight, energy, and blood sugar levelsResearchers review the effects of dietary protein on energy intake, appetite, and postprandial glycemia.
Read more »
 New compound shows promise in Alzheimer’s preclinical modelsA multidisciplinary team of scientists led by Kurt Brunden, Ph.D., at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, and Carlo Ballatore, Ph.D., at University of California San Diego, has been awarded a $6.
New compound shows promise in Alzheimer’s preclinical modelsA multidisciplinary team of scientists led by Kurt Brunden, Ph.D., at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, and Carlo Ballatore, Ph.D., at University of California San Diego, has been awarded a $6.
Read more »
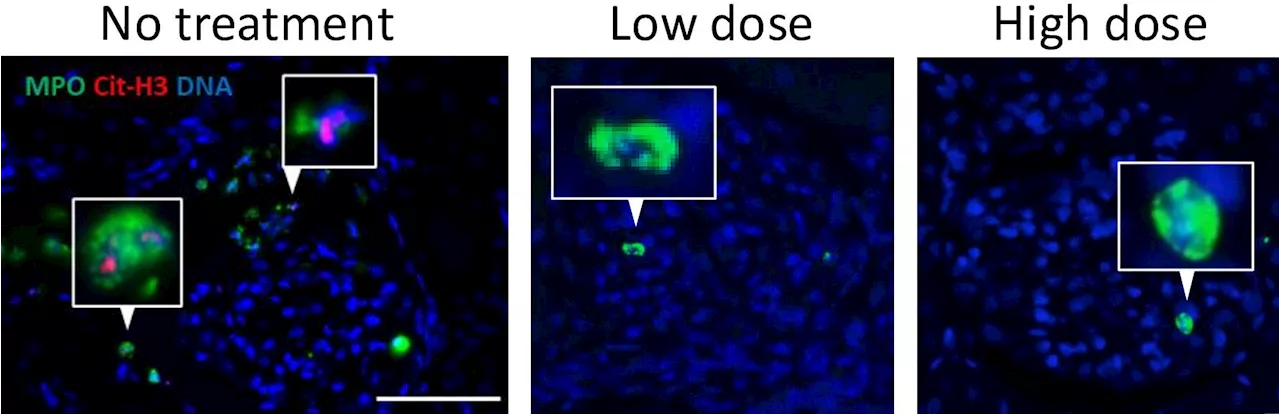 New compound shows great potential for patients with neutrophil-associated inflammationA newly developed compound that reduces harmful inflammation caused by overactive neutrophils in rats shows great potential as a safer treatment for various inflammatory diseases in humans.
New compound shows great potential for patients with neutrophil-associated inflammationA newly developed compound that reduces harmful inflammation caused by overactive neutrophils in rats shows great potential as a safer treatment for various inflammatory diseases in humans.
Read more »
 New antibacterial compound shows promise for preventing periodontal diseasePeriodontal disease is an inflammatory disease caused by a periodontal pathogenic bacteria infection that affects oral and internal health.
New antibacterial compound shows promise for preventing periodontal diseasePeriodontal disease is an inflammatory disease caused by a periodontal pathogenic bacteria infection that affects oral and internal health.
Read more »
