A new study from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) reveals that pregnancy causes significant physical changes in the brains of 94% of mothers. These changes, driven by pregnancy hormones, primarily affect areas associated with social cognition, emotional processing, and maternal bonding. Researchers suggest these adaptations help mothers respond instinctively to their baby's needs and strengthen their emotional connection.
Share on tumblrfrom the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona found that pregnancy physically changes 94% of a mother’s brain, particularly in areas linked to social cognition, emotional processing, and maternal bonding.
The findings confirmed that pregnancy leads to a reduction of up to 4.9% in grey matter volume, particularly in areas involved in social interactions and emotional regulation. The results showed that the brain changes were primarily biological, rather than caused by sleep deprivation or new responsibilities.The research found that these brain changes closely follow fluctuations in pregnancy hormones, particularly two forms of oestrogen—estriol-3-sulfate and estrone-sulfate.
Instead of being a sign of cognitive decline, these changes are likely an evolutionary advantage—helping mothers tune in to their baby’s needs and emotions.By mapping out these changes, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of how pregnancy impacts maternal mental health.
PREGNANCY BRAIN CHANGES MATERNAL BONDING HORMONES POSTPARTUM RECOVERY
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Pregnancy Induces U-Shaped Brain Structural Changes Linked to Hormones and Maternal AttachmentA new study published in Nature Communications reveals that pregnancy causes a reduction in gray matter volume in the brain, primarily in regions linked to social cognition, with partial recovery postpartum. This U-shaped trajectory is associated with fluctuations in estrogen levels. The research, led by scientists at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), provides valuable insights into the neurobiology of pregnancy and its impact on maternal bonding.
Pregnancy Induces U-Shaped Brain Structural Changes Linked to Hormones and Maternal AttachmentA new study published in Nature Communications reveals that pregnancy causes a reduction in gray matter volume in the brain, primarily in regions linked to social cognition, with partial recovery postpartum. This U-shaped trajectory is associated with fluctuations in estrogen levels. The research, led by scientists at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), provides valuable insights into the neurobiology of pregnancy and its impact on maternal bonding.
Read more »
 Pregnancy triggers profound brain changes, enhancing maternal instincts and mental healthA groundbreaking study reveals that pregnancy leads to a U-shaped pattern in gray matter volume, driven by hormonal changes and linked to maternal attachment.
Pregnancy triggers profound brain changes, enhancing maternal instincts and mental healthA groundbreaking study reveals that pregnancy leads to a U-shaped pattern in gray matter volume, driven by hormonal changes and linked to maternal attachment.
Read more »
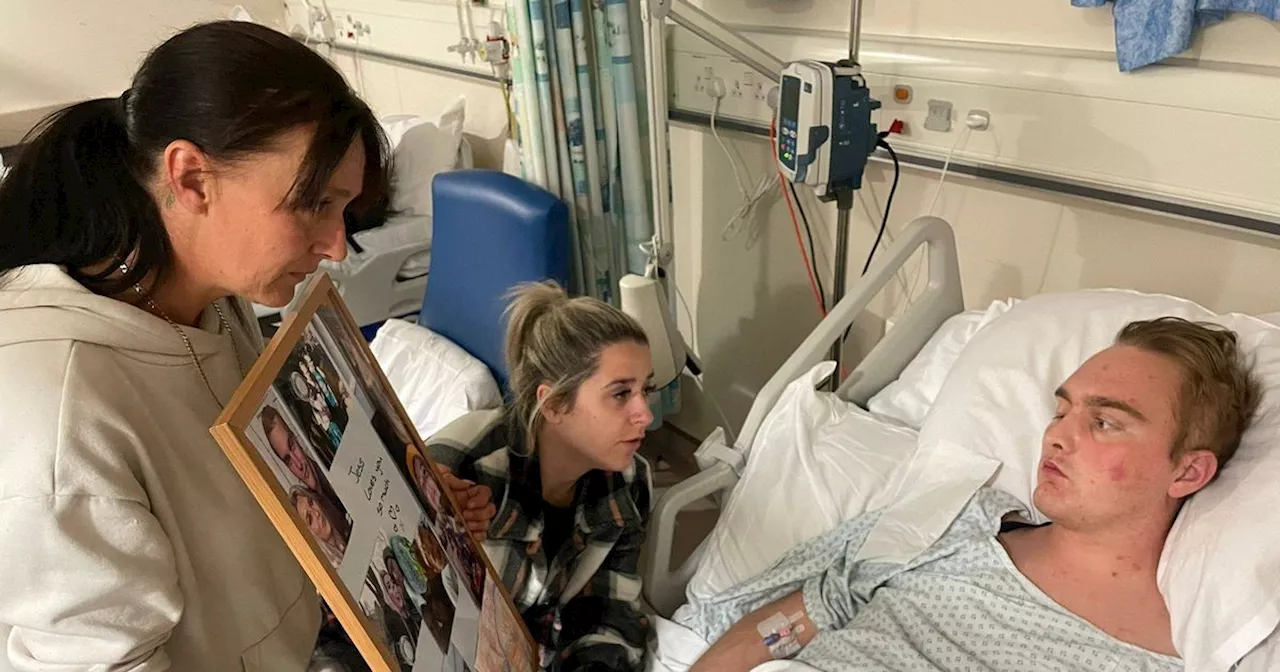 Young Man Left With Permanent Brain Damage After Rare Brain InflammationMartin Griffiths, a 25-year-old man, suffered from a rare form of brain inflammation called primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) after experiencing a sudden headache. Initially diagnosed with a stroke, he was later given just three to six months to live. Despite his family's hope for recovery, Martin is now living in a care home with permanent brain damage.
Young Man Left With Permanent Brain Damage After Rare Brain InflammationMartin Griffiths, a 25-year-old man, suffered from a rare form of brain inflammation called primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) after experiencing a sudden headache. Initially diagnosed with a stroke, he was later given just three to six months to live. Despite his family's hope for recovery, Martin is now living in a care home with permanent brain damage.
Read more »
 Only people with a high IQ can solve this hidden woman optical illusionTest your brain this January with this brain-twisting optical illusion.
Only people with a high IQ can solve this hidden woman optical illusionTest your brain this January with this brain-twisting optical illusion.
Read more »
 New Brain Stem Cell Discovery Could Lead to Better Treatments for GlioblastomaScientists at the University of California - San Francisco have discovered a new type of stem cell in the young brain that has the potential to form cells found in tumors. This breakthrough could explain how adult brain cells use developmental processes to fuel the rapid growth seen in deadly brain cancers like glioblastoma. The findings, published in Nature, provide a detailed map of human brain development and could also shed light on the origins of autism.
New Brain Stem Cell Discovery Could Lead to Better Treatments for GlioblastomaScientists at the University of California - San Francisco have discovered a new type of stem cell in the young brain that has the potential to form cells found in tumors. This breakthrough could explain how adult brain cells use developmental processes to fuel the rapid growth seen in deadly brain cancers like glioblastoma. The findings, published in Nature, provide a detailed map of human brain development and could also shed light on the origins of autism.
Read more »
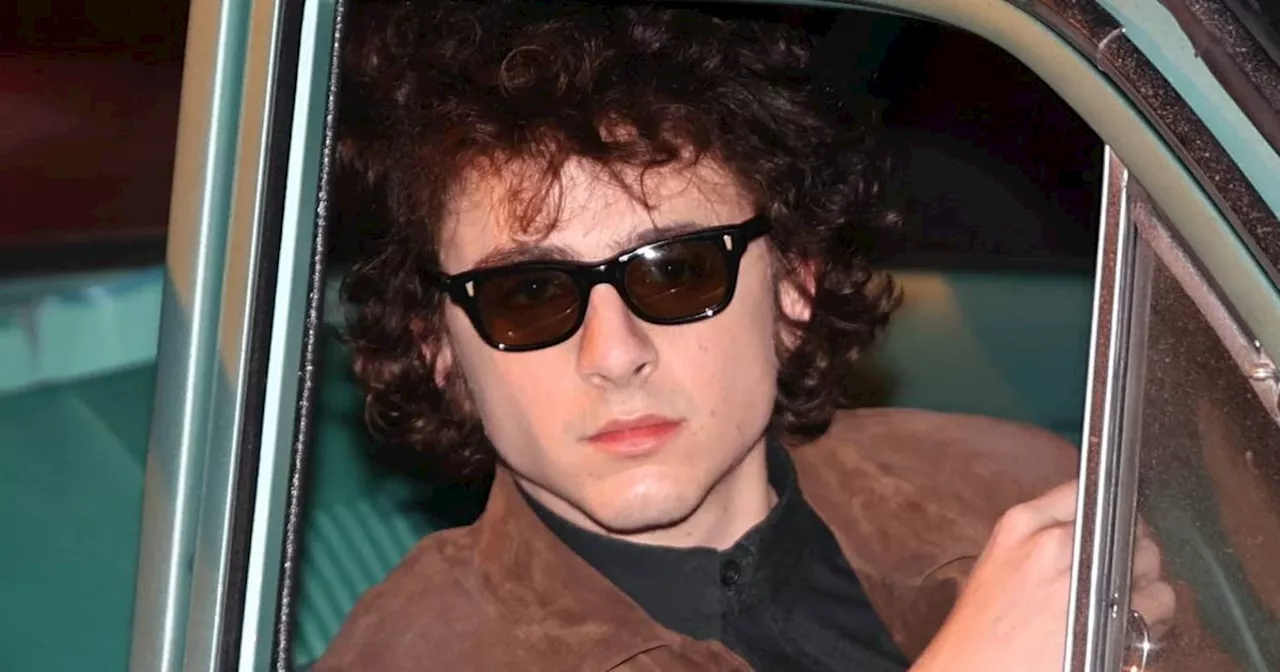 Timothée Chalamet Reveals Five-Year Obsession in Preparing for Bob Dylan BiopicTimothée Chalamet's highly anticipated biopic, 'A Complete Unknown', sees him portraying the iconic Bob Dylan. Chalamet discusses his intensive five-year preparation process, which involved live singing, guitar playing, and deep research into Dylan's life and music. He reveals his deep admiration for Dylan's artistry and the profound impact his music had on him.
Timothée Chalamet Reveals Five-Year Obsession in Preparing for Bob Dylan BiopicTimothée Chalamet's highly anticipated biopic, 'A Complete Unknown', sees him portraying the iconic Bob Dylan. Chalamet discusses his intensive five-year preparation process, which involved live singing, guitar playing, and deep research into Dylan's life and music. He reveals his deep admiration for Dylan's artistry and the profound impact his music had on him.
Read more »
