Researchers found that while both antidepressants and group running therapy effectively improved mental health in patients with anxiety and depression, running therapy had significantly better outcomes for physical health indicators.
By Dr. Chinta SidharthanMay 26 2024Reviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc. In a recent study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, a team of researchers from the Netherlands compared the effects of antidepressants and exercise therapy in the form of group-based running on the physical and mental health of patients with anxiety disorder s and depression.
Exercise therapy has been recommended as an alternate form of treatment for anxiety and depression. Studies have found that exercise interventions for cases of mild to moderate depression are as effective as psychotherapy and antidepressants. Furthermore, for cases of severe depression, exercise therapy continues to be helpful as a complementary therapy.
The study examined mental health outcomes such as diagnosis status and severity of symptoms, while physical health outcomes included indicators of immune and metabolic health, variability in heart rate, lung function, body weight, fitness, and hand grip strength. The researchers hypothesized that the mental health outcomes would not be very different for the two interventions, but the ones related to physical health would differ.
Related StoriesThe other intervention included 45 minutes of supervised outdoor running two to three times each week for 16 weeks. All the participants undergoing this intervention wore a heart rate monitor, which helped confirm adherence to the exercise regimen. Physical health characteristics such as body weight, waist circumference, heart rate, variability in heart rate, and blood pressure differed significantly between the two interventions. The group undergoing running therapy showed more improvements in all these factors than the one being treated with antidepressants. The C-reactive protein and triglyceride levels were also found to be different between running therapy and antidepressant interventions.
Running Antidepressant Anxiety Anxiety Disorder Blood Blood Pressure C-Reactive Protein Depression Exercise Heart Heart Rate Immunity Protein Psychotherapy
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers discover how gut microbes influence social behavior in miceFor people with autism, constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal pain often go along with the social struggles and repetitive behaviors that define the condition.
Researchers discover how gut microbes influence social behavior in miceFor people with autism, constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal pain often go along with the social struggles and repetitive behaviors that define the condition.
Read more »
 Researchers partner with children's hospital on new heart surgery planning toolCardiologists and surgeons could soon have a new mobile augmented reality (AR) tool to improve collaboration in surgical planning.
Researchers partner with children's hospital on new heart surgery planning toolCardiologists and surgeons could soon have a new mobile augmented reality (AR) tool to improve collaboration in surgical planning.
Read more »
 Researchers create human aortic aneurysm model to advance disease understanding, treatment testingUsing human cells in laboratory rats, Michigan Medicine researchers have developed a functional model of thoracic aortic aneurysm, creating opportunities for more effective understanding of disease development and treatments for the potentially fatal condition, a study suggests.
Researchers create human aortic aneurysm model to advance disease understanding, treatment testingUsing human cells in laboratory rats, Michigan Medicine researchers have developed a functional model of thoracic aortic aneurysm, creating opportunities for more effective understanding of disease development and treatments for the potentially fatal condition, a study suggests.
Read more »
 Researchers reveal the double-edged-sword effect of overconfidence on gamblingAs a popular form of entertainment in modern society, the gambling industry has been hailed as 'the heart of the economy in the post-industrial era.' However, gambling poses serious risks, not only to the financial and psychological well-being of individuals, but also to social stability.
Researchers reveal the double-edged-sword effect of overconfidence on gamblingAs a popular form of entertainment in modern society, the gambling industry has been hailed as 'the heart of the economy in the post-industrial era.' However, gambling poses serious risks, not only to the financial and psychological well-being of individuals, but also to social stability.
Read more »
 Researchers find 13% reduction in asthma in children born in an urban low emission zoneFor the first time, the long-term benefits of urban low emission zones for children's health have been scientifically quantified.
Researchers find 13% reduction in asthma in children born in an urban low emission zoneFor the first time, the long-term benefits of urban low emission zones for children's health have been scientifically quantified.
Read more »
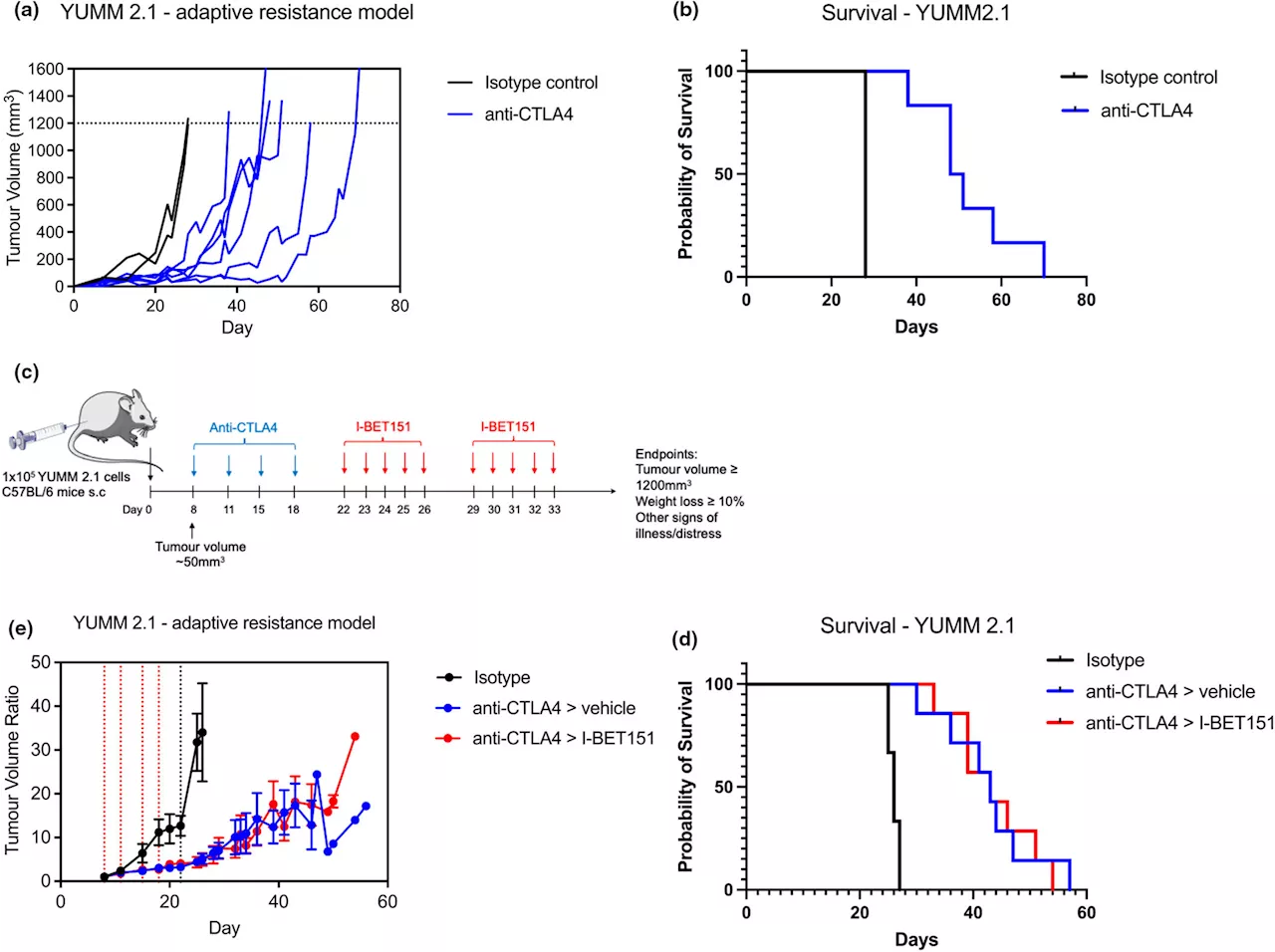 Researchers use dual drug strategy to advance melanoma treatment against resistanceResearch conducted by the Centenary Institute has revealed a promising new approach to tackling melanoma, an aggressive form of skin cancer notorious for its resistance to conventional treatments.
Researchers use dual drug strategy to advance melanoma treatment against resistanceResearch conducted by the Centenary Institute has revealed a promising new approach to tackling melanoma, an aggressive form of skin cancer notorious for its resistance to conventional treatments.
Read more »
