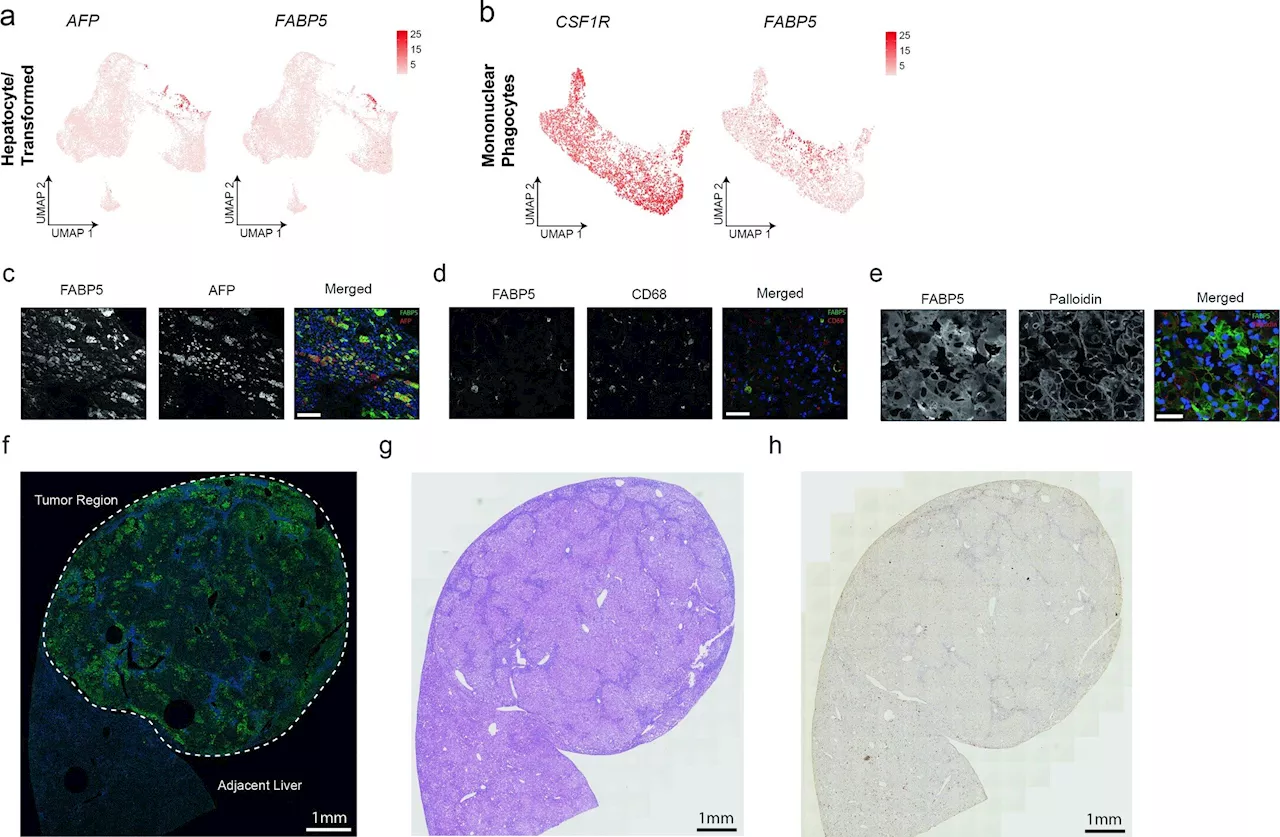
Metabolic diseases like obesity can increase the risk of developing liver cancer, research has shown. But how one disease predisposes to the other is unclear. In a new study, Yale researchers uncovered a key role played by a molecule called fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) and found that inhibiting it blocked tumor progression in many cases.
Study identifies driver of liver cancer that could be target for treatment retrieved 26 April 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-04-driver-liver-cancer-treatment.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Nov 30, 2023Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Study reveals genetic drivers of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseIn the largest study of its kind, researchers from the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), part of City of Hope, have identified genes that appear to drive the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH).
Study reveals genetic drivers of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseIn the largest study of its kind, researchers from the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), part of City of Hope, have identified genes that appear to drive the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH).
Read more »
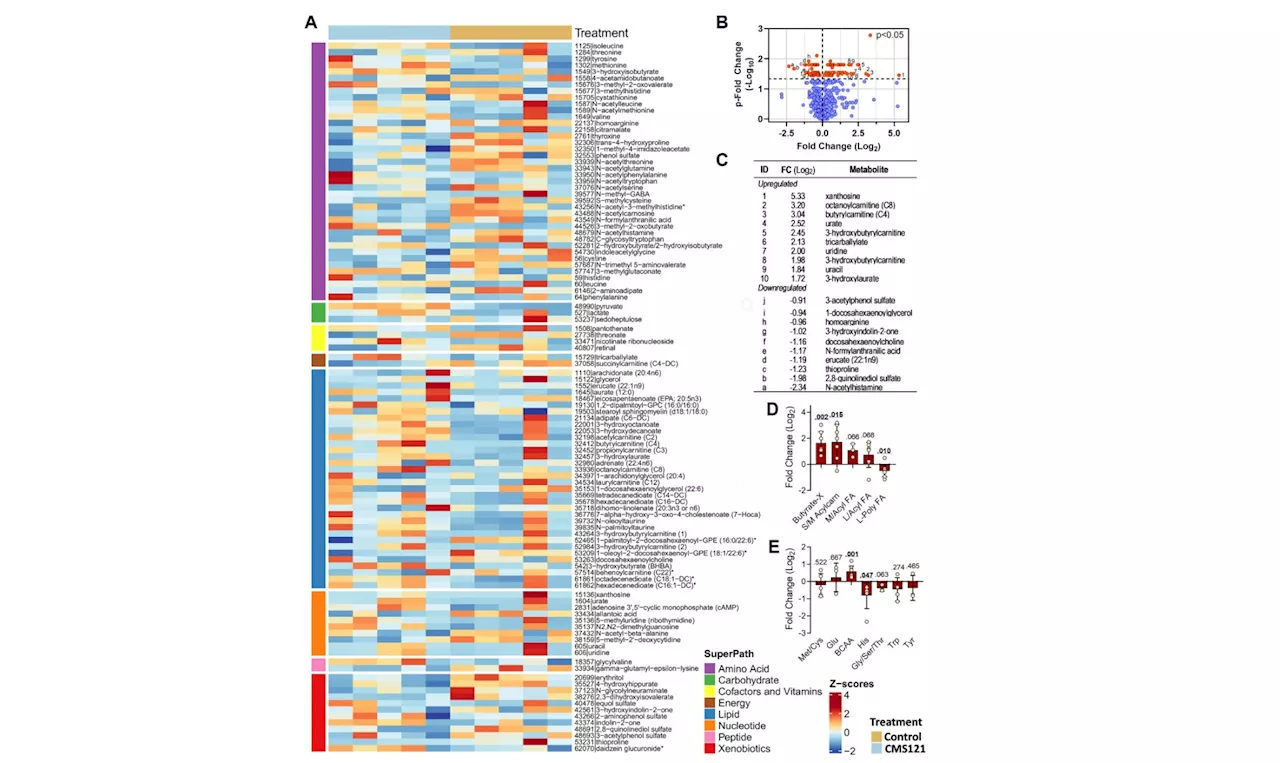 CMS121 mitigates aging-related obesity and metabolic dysfunction: StudyA new research paper titled 'CMS121: a novel approach to mitigate aging-related obesity and metabolic dysfunction' has been published in Aging.
CMS121 mitigates aging-related obesity and metabolic dysfunction: StudyA new research paper titled 'CMS121: a novel approach to mitigate aging-related obesity and metabolic dysfunction' has been published in Aging.
Read more »
 Metabolic markers tied to increased risk of depression and anxiety, study findsComprehensive study within a large Swedish cohort links elevated glucose and triglyceride levels to an increased risk of developing depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, while higher HDL-C levels seem protective, suggesting a significant connection between metabolic health and psychiatric conditions.
Metabolic markers tied to increased risk of depression and anxiety, study findsComprehensive study within a large Swedish cohort links elevated glucose and triglyceride levels to an increased risk of developing depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, while higher HDL-C levels seem protective, suggesting a significant connection between metabolic health and psychiatric conditions.
Read more »
 Study reveals metabolic markers linked to long COVID-19 severityLong COVID-19, or post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), is a global health phenomenon characterized by persistent symptoms following the acute phase of COVID-19.
Study reveals metabolic markers linked to long COVID-19 severityLong COVID-19, or post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), is a global health phenomenon characterized by persistent symptoms following the acute phase of COVID-19.
Read more »
 Study shows metabolic health before vaccination determines effectiveness of anti-flu responseMetabolic health (normal blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels, among other factors) influences the effectiveness of influenza vaccinations. Vaccination is known to be less effective in people with obesity compared to those with a healthier body mass index (BMI), but St.
Study shows metabolic health before vaccination determines effectiveness of anti-flu responseMetabolic health (normal blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels, among other factors) influences the effectiveness of influenza vaccinations. Vaccination is known to be less effective in people with obesity compared to those with a healthier body mass index (BMI), but St.
Read more »
 Survey unveils India's rising tide of metabolic diseasesStudy reveals high rates of non-communicable metabolic diseases across India, with notable differences in prevalence between urban and rural areas and among different Indian states.
Survey unveils India's rising tide of metabolic diseasesStudy reveals high rates of non-communicable metabolic diseases across India, with notable differences in prevalence between urban and rural areas and among different Indian states.
Read more »