In this study, researchers build evaluation tasks from naturally-occurring textual resources.
Author: Mingda Chen. Table of Links Abstract Acknowledgements 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Overview 1.2 Contributions 2 BACKGROUND 2.1 Self-Supervised Language Pretraining 2.2 Naturally-Occurring Data Structures 2.3 Sentence Variational Autoencoder 2.4 Summary 3 IMPROVING SELF-SUPERVISION FOR LANGUAGE PRETRAINING 3.1 Improving Language Representation Learning via Sentence Ordering Prediction 3.2 Improving In-Context Few-Shot Learning via Self-Supervised Training 3.
is a challenging testbed for abstractive summarization. To evaluate the faithfulness of the generated stories to the brief summaries, we propose a metric that uses the perplexities from the summarization model trained on our dataset. Empirically, we characterize the dataset with several nearest neighbour methods and oracle models, finding that the use of the brief summaries and the character descriptions generally benefits model performance.
from two fan-contributed websites: Fandom and TVMegaSite . We collect brief summaries and detailed episode recaps for several long-running soap operas from TVMegaSite and other TV shows from Fandom. We collect character descriptions from Fandom. Since the pages on Fandom have hyperlinks pointing to the character pages, we use the hyperlinks to connect episodes to the characters involved. For TVMegaSite, where there are no such hyperlinks, we use string matching to find the characters.
has character descriptions as extra constraints, making the task of generating the reference stories from the inputs less open-ended and therefore more feasible. Since often have detailed descriptions about environments and character utterances, whereas the stories in are unfinished. The stories in our dataset are created and refined by professional screenwriters . Stories in
than lacks direction interactions among characters. We quantify this phenomenon in into a coherent narrative. Summarization. By considering generating the brief summary from the detailed episode recap, we can view poses several challenges for story generation models. The first challenge stems from the long lengths of the inputs and outputs. Specifically, the average instance in
from fan-contributed websites, which allows us to collect 26k episode recaps covering a variety of genres. An example from and compare it to other story generation datasets. An instance in , finding that FD covers far more genres than TMS with the most frequent occupying only 15% of episodes. We randomly split the datasets into train/dev/test sets. For TMS, we additionally filter out instances if the overlap ratio of TV show characters appearing in the summary and the detailed recap is lower than 85%. This extra filtering step ensures alignment between the summaries and detailed recaps. See Table 6.27 for the train/dev/test sizes for FD and TMS. Dataset Comparison.
. Below we compare our dataset to , it also prevents the task from conflating generating events and generating other kinds of details in story generation. Due to the fact that the plots in mostly narrate events that happened without these details. While this leads to shorter stories in , it also prevents the task from conflating generating events and generating other kinds of details in story generation. Due to the fact that the plots in
are unfinished. The stories in our dataset are created and refined by professional screenwriters . Stories in than lacks direction interactions among characters. We quantify this phenomenon in are turn-based, where each turn is written from the perspective of a particular character and is composed by one player, so the stories often lack direct interactions among characters, unlike
than than lacks direction interactions among characters. We quantify this phenomenon in can potentially complement those from
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Tailoring Textual Resources for Evaluation Tasks: Long-Form Data-to-Text GenerationIn this study, researchers build evaluation tasks from naturally-occurring textual resources.
Tailoring Textual Resources for Evaluation Tasks: Long-Form Data-to-Text GenerationIn this study, researchers build evaluation tasks from naturally-occurring textual resources.
Read more »
 Tailoring Textual Resources for Evaluation Tasks: Long-Form Text SummarizationIn this study, researchers build evaluation tasks from naturally-occurring textual resources.
Tailoring Textual Resources for Evaluation Tasks: Long-Form Text SummarizationIn this study, researchers build evaluation tasks from naturally-occurring textual resources.
Read more »
 Leveraging Natural Supervision: Tailoring Textual Resources for Evaluation TasksIn this study, researchers build evaluation tasks from naturally-occurring textual resources.
Leveraging Natural Supervision: Tailoring Textual Resources for Evaluation TasksIn this study, researchers build evaluation tasks from naturally-occurring textual resources.
Read more »
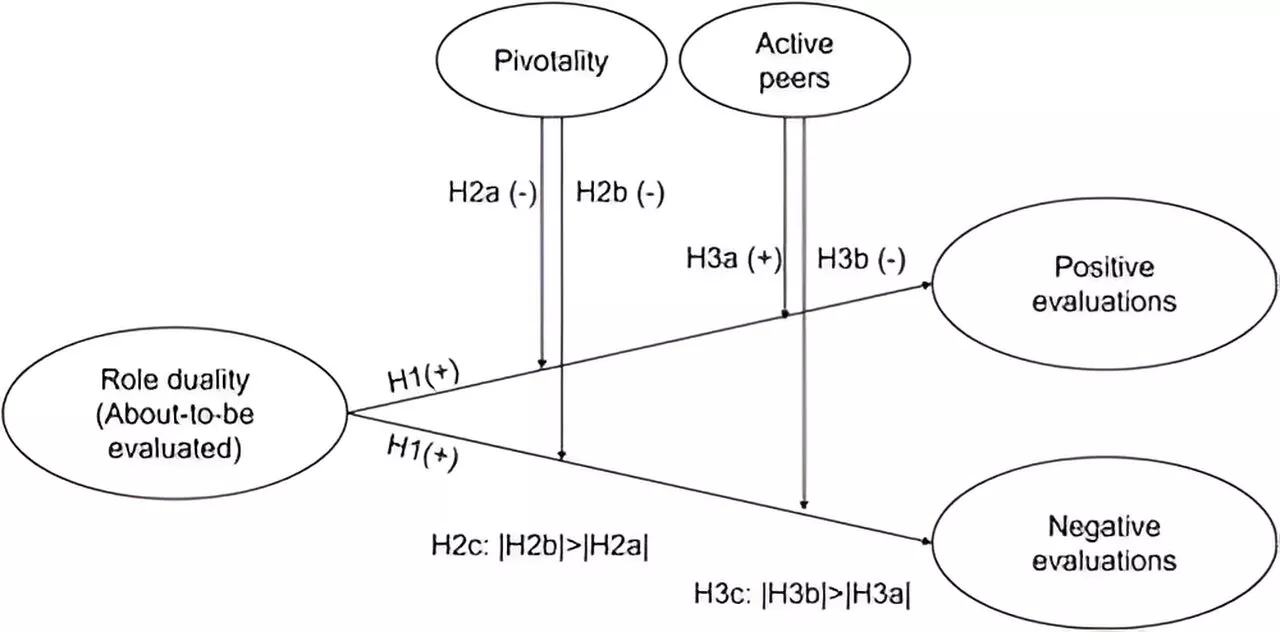 Study finds individuals less likely to evaluate peers negatively if facing evaluation themselvesNew research from ESMT Berlin finds that individuals strategically select the colleagues they evaluate, and the evaluation they give, based on how they want to be perceived. The research was published in the journal Organization Science.
Study finds individuals less likely to evaluate peers negatively if facing evaluation themselvesNew research from ESMT Berlin finds that individuals strategically select the colleagues they evaluate, and the evaluation they give, based on how they want to be perceived. The research was published in the journal Organization Science.
Read more »
 25 Best Petite Jeans for Women 2024 That Don’t Need TailoringOne Vogue editor searches for the best petite jeans for women, from high-rise styles to straight-leg fits. Shop her go-to finds that don’t need alterations.
25 Best Petite Jeans for Women 2024 That Don’t Need TailoringOne Vogue editor searches for the best petite jeans for women, from high-rise styles to straight-leg fits. Shop her go-to finds that don’t need alterations.
Read more »
 Independent evaluation of mental competency granted for accused killer of El Cajon dentistRyan Hill is stoked to be in San Diego! He’s coming to the area from Sacramento. So, he only had to shuffle his area codes around a little bit, trading the 916 for the 619.
Independent evaluation of mental competency granted for accused killer of El Cajon dentistRyan Hill is stoked to be in San Diego! He’s coming to the area from Sacramento. So, he only had to shuffle his area codes around a little bit, trading the 916 for the 619.
Read more »
