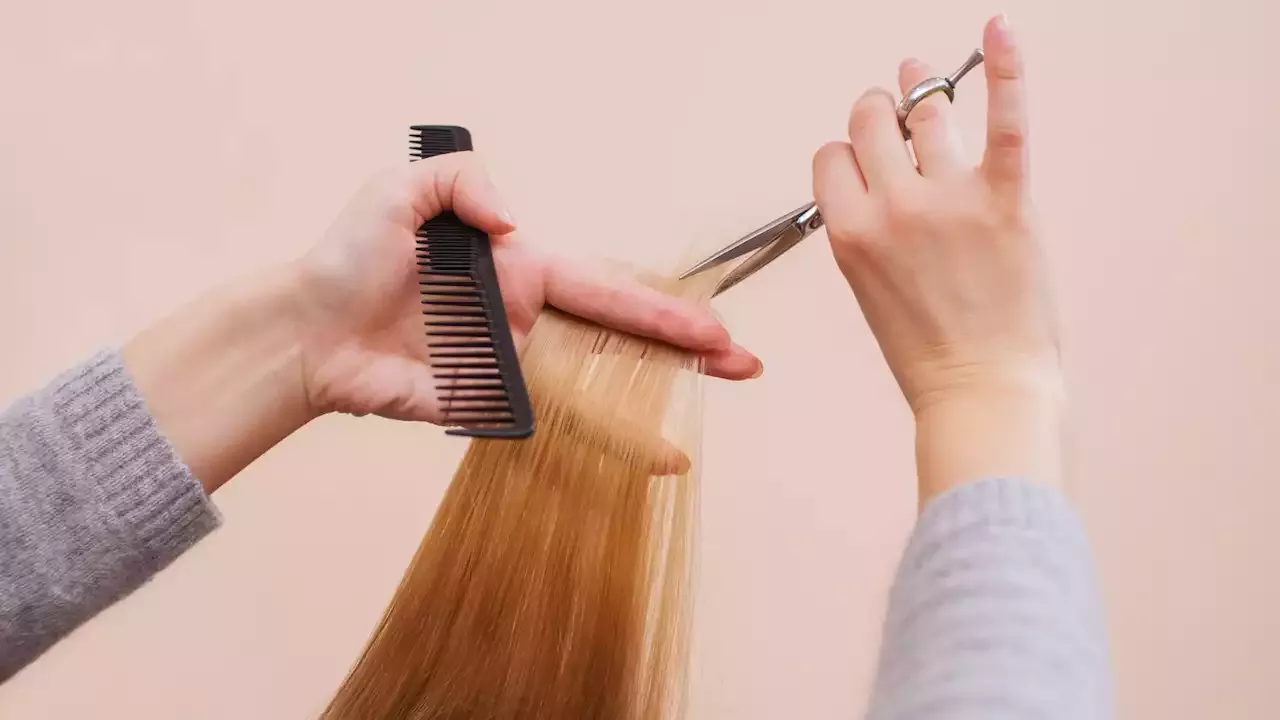
Those working in sales, retail, clothing and construction industries could also carry a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer, a new study suggests
They also compared this data with the Canadian job-exposure matrix to examine any potential workplace exposures - for example, if they are more likely to come in contact with a certain chemical while at work.
Those who had worked as a hairdresser, barber or beautician appeared to have a three-fold higher risk. Shop assistants and sales people had a 45% increased risk while those who make or alter clothes appeared to have an 85% increased risk.The researchers said that those found to have a higher risk were also more likely to be exposed to a number of"agents" including cosmetic talc, ammonia, hydrogen peroxide, hair dust, synthetic fibres, polyester fibres, organic dyes, and pigments and bleaches.
"Further population-based research is needed to evaluate possible hazards for female workers and occupations commonly held by women."Cancer patients face worsening delaysIn a linked editorial, academics from the National Cancer Institute in Maryland in the US point out that women are under-represented in"occupational cancer research studies".
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Family history and breast cancer risk for Asian women: a systematic review and meta-analysis - BMC MedicineBackground Studies of women of European ancestry have shown that the average familial relative risk for first-degree relatives of women with breast cancer is approximately twofold, but little is known for Asian women. We aimed to provide evidence for the association between family history and breast cancer risk for Asian women by systematically reviewing published literature. Methods Studies reporting the familial relative risk of breast cancer for Asian women were searched in three online databases and complemented by a manual search. Odds ratios (ORs) for the association between family history and breast cancer risk were pooled across all included studies and by subgroups in terms of the type of family history, age, menopausal status and geographical region. Results The pooled OR for women who have a first-degree relative with breast cancer was 2.46 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.03, 2.97). There was no evidence that the familial risk differed by the type of affected relative (mother versus sisters), the woman’s age ( 0.3). The pooled ORs for women of Asian ancestry with a family history in any relative were similar for those living in non-Asian countries (2.26, 95% CI: 1.42, 3.59) compared with those living in Asian countries (2.18, 95% CI: 1.85, 2.58). Conclusions Family history of breast cancer is associated with an approximately twofold relative risk of breast cancer for Asian women, which is of similar magnitude to that observed for women of European ancestry. This implies that similar familial factors are implicated in breast cancer risk between women of European and Asian ancestries. Genetic factors are likely to play a substantial role in explaining the breast cancer familial risk for Asian women, as similar risks were observed across different living environments and cultures.
Family history and breast cancer risk for Asian women: a systematic review and meta-analysis - BMC MedicineBackground Studies of women of European ancestry have shown that the average familial relative risk for first-degree relatives of women with breast cancer is approximately twofold, but little is known for Asian women. We aimed to provide evidence for the association between family history and breast cancer risk for Asian women by systematically reviewing published literature. Methods Studies reporting the familial relative risk of breast cancer for Asian women were searched in three online databases and complemented by a manual search. Odds ratios (ORs) for the association between family history and breast cancer risk were pooled across all included studies and by subgroups in terms of the type of family history, age, menopausal status and geographical region. Results The pooled OR for women who have a first-degree relative with breast cancer was 2.46 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.03, 2.97). There was no evidence that the familial risk differed by the type of affected relative (mother versus sisters), the woman’s age ( 0.3). The pooled ORs for women of Asian ancestry with a family history in any relative were similar for those living in non-Asian countries (2.26, 95% CI: 1.42, 3.59) compared with those living in Asian countries (2.18, 95% CI: 1.85, 2.58). Conclusions Family history of breast cancer is associated with an approximately twofold relative risk of breast cancer for Asian women, which is of similar magnitude to that observed for women of European ancestry. This implies that similar familial factors are implicated in breast cancer risk between women of European and Asian ancestries. Genetic factors are likely to play a substantial role in explaining the breast cancer familial risk for Asian women, as similar risks were observed across different living environments and cultures.
Read more »
 How B-cells and androgens contribute to the development of PCOSHow B-cells and androgens contribute to the development of PCOS PCOS research Bcell AndrogenReceptor ImmunoglobulinM Autoimmune Comorbidities HormonalImbalance WomenzHealth eLife
How B-cells and androgens contribute to the development of PCOSHow B-cells and androgens contribute to the development of PCOS PCOS research Bcell AndrogenReceptor ImmunoglobulinM Autoimmune Comorbidities HormonalImbalance WomenzHealth eLife
Read more »
 Do system-level DOAC therapy management services affect anticoagulation outcomes for AF patients compared to usual care?Do system-level DOAC therapy management services affect anticoagulation outcomes for AF patients compared to usual care? JAMANetworkOpen DOAC therapy anticoagulation AF patients
Do system-level DOAC therapy management services affect anticoagulation outcomes for AF patients compared to usual care?Do system-level DOAC therapy management services affect anticoagulation outcomes for AF patients compared to usual care? JAMANetworkOpen DOAC therapy anticoagulation AF patients
Read more »
 How has the prevalence of psychological distress in the adult population of England changed since 2020?How has the prevalence of psychological distress in the adult population of England changed since 2020? JAMANetworkOpen ucl distress psychological physchologicaldistress mentalhealth covid COVID19
How has the prevalence of psychological distress in the adult population of England changed since 2020?How has the prevalence of psychological distress in the adult population of England changed since 2020? JAMANetworkOpen ucl distress psychological physchologicaldistress mentalhealth covid COVID19
Read more »
 The causative role of age-associated pre-existing senescent cells on COVID-19 severityThe causative role of age-associated pre-existing senescent cells on COVID-19 severity NatureAging aging covid COVID19 SARSCov2 senescentcells lungs
The causative role of age-associated pre-existing senescent cells on COVID-19 severityThe causative role of age-associated pre-existing senescent cells on COVID-19 severity NatureAging aging covid COVID19 SARSCov2 senescentcells lungs
Read more »
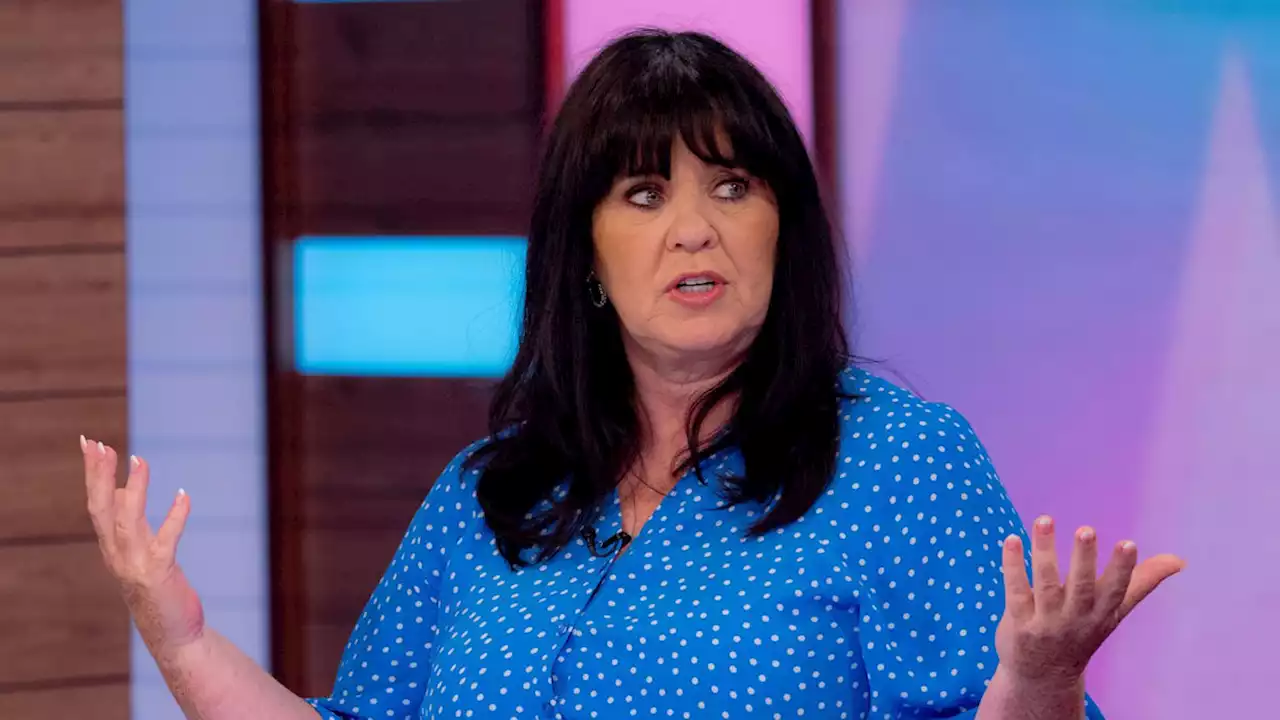 Loose Women's Coleen Nolan reveals where she 'went wrong' in previous relationshipNolan Sisters singer Coleen recently revealed she was in a new relationship
Loose Women's Coleen Nolan reveals where she 'went wrong' in previous relationshipNolan Sisters singer Coleen recently revealed she was in a new relationship
Read more »
